Home »
Misc »
How to prepare for high school basketball
How to prepare for high school basketball
How To Prepare Players for High School Basketball, Coach's Clipboard
Home >
Coaching >
How Youth Coaches Can Better Prepare Their Players for High School Basketball
From the Coach’s Clipboard Basketball Playbook
Kyle Ohman is the co-creator of Basketballhq.com a basketball training website designed for coaches and players. He was a thousand point scorer at Liberty University (div. 1), was ranked the 19th best shooter in the country by Fox Sports going into his senior year.
Kyle has also played professionally in Spain. Most recently he coached a high school team out of Brandon, FL that played on a national level and beat the 12th ranked team in the nation. Coach Kyle has a promising career in the basketball industry as a coach and an individual trainer.
When a high school coach is looking to set their team roster, they must take into account a lot of different factors.![]() There are the obvious factors like points, assists, rebounds, etc., which most people outside of the game focus on, but there are also other areas that are always being evaluated as well. There is attitude, effort, IQ, etc. that must also be evaluated as well.
There are the obvious factors like points, assists, rebounds, etc., which most people outside of the game focus on, but there are also other areas that are always being evaluated as well. There is attitude, effort, IQ, etc. that must also be evaluated as well.
The goal of this article is to highlight some of these other areas that high school coaches will be focusing on. That way, as a middle school or youth basketball coach, you will be able to better prepare your players for being able to play at the next level. And, even though this article is going to be geared for coaches, it can still be an excellent checklist for players to focus on as well.
So here are eight different areas that you should be focusing on with your players and making sure that you are holding them accountable in.
Attitude and Effort
This key is non-negotiable. As a coach, you already fully understand this, but especially as players get older, there is no reason why they shouldn't be giving their best effort every day and doing it with a great attitude. Even when players aren't "feeling it," they need to be giving their best. As a coach, this is something that you need to preach on a daily basis. You need to make sure that you don't allow your players to slip by with less than their best attitude and effort. If you allow players to have a bad attitude or give poor effort when they are younger, it will only be that much more of a bad habit that they will have to break later on down the road.
Even when players aren't "feeling it," they need to be giving their best. As a coach, this is something that you need to preach on a daily basis. You need to make sure that you don't allow your players to slip by with less than their best attitude and effort. If you allow players to have a bad attitude or give poor effort when they are younger, it will only be that much more of a bad habit that they will have to break later on down the road.
Basketball IQ
Doing basketball drills and different moves are great, but it is also vital that you are teaching your players how to think the game as well. This is one of the key areas that I focus on as a Basketball Trainer in Tampa and it has paid out big for the players I have worked with. It is not just enough to do a drill, you must also teach how it is applied to the game.
So as you teach different moves or actions, take the time to explain and breakdown why they should be done the way that they are done. Teach your players how to read different situations and show them what they should be looking for. And, if this is not one of your strong suits, continue to learn yourself.
Teach your players how to read different situations and show them what they should be looking for. And, if this is not one of your strong suits, continue to learn yourself.
Quick Learner
There are only so many minutes in practice or workouts, coaches need players that are quick learners. The longer a coach has to go over a specific action, the less time they have to work on other key areas. So the quicker a player is able to learn, the more a coach is going to value them.
Also, a coach wants to be able to know that mid-game or late-game, they are able to throw in a wrinkle and their players are going to be able to understand and execute. As a youth coach, challenge your players to stay locked in when you are talking and have them listen with both their ears and their eyes, this will really help with the learning process.
Buying Into a Role
Great teams are filled with players that execute THEIR role extremely well. Coaches want players that understand this and are willing to buy into the role that is best going to help the team. However, that doesn't mean that roles can't change. Encourage your players to work and develop their game so that they can have a bigger role, but also challenge them to buy into mastering the role that is going to best help the team.
Coaches want players that understand this and are willing to buy into the role that is best going to help the team. However, that doesn't mean that roles can't change. Encourage your players to work and develop their game so that they can have a bigger role, but also challenge them to buy into mastering the role that is going to best help the team.
Make Shots
I know, I know, in the opening paragraph I said areas "outside of scoring." It is important to note though, that coaches are looking for players that are consistent shot makers. It doesn't mean that they have to put up a ton of points, but it means that they can knock down an open shot when the ball is passed to them. Depending on the player, this is going to be different types of shots as well. It also means that players need to value every shot that they shoot and not force up bad shots that have a low percentage chance of going in.
Take Care of the Ball
Turnovers will kill an offense and allow for easy baskets for the other team; that cannot happen. Teach your players to be strong with the ball, use pass fakes, and play under control. If a coach is able to trust a player to take care of the ball, that player will be able to add a ton of value to their stock. On the flip side, if a player is constantly turning the ball over, they are not going to be able to play. Work with your players and teach them to be confident with the ball, and help them learn to make the right reads as they make passes.
Teach your players to be strong with the ball, use pass fakes, and play under control. If a coach is able to trust a player to take care of the ball, that player will be able to add a ton of value to their stock. On the flip side, if a player is constantly turning the ball over, they are not going to be able to play. Work with your players and teach them to be confident with the ball, and help them learn to make the right reads as they make passes.
Creating for Others
The better the competition, the more being able to create for others comes into play. It isn't enough for a player to just be able to create for themselves, they must also help other teammates get shots as well. Also, if a player has a balanced approach to being able to create for themselves and also teammates, they will keep the help defense honest. So really lock in and focus on this with your younger players. Teach them how to be able to drive and kick, make the extra pass, set a great screen, and whatever else will help to create for teammates.
Conditioning
A player's conditioning level is an easy indicator for a coach on their level of commitment to being a part of the team. If a player shows up out of shape, it shows that they are not valuing what the team is trying to do. It is a different story if a player is coming off of an injury or something like that, but if there is not a legitimate excuse, there is no reason why every player shouldn't be in shape. So make sure to challenge your players to always be in shape, especially when they show up at the beginning of a season.
Conclusion
As a basketball coach, you are most likely already focusing on a lot of these different areas with your players, but it is good to have a reminder of what should be valued. As a coach myself, I am constantly having to refocus and remind myself of what is most important.
It is also important that as a coach you are continuing to develop your coaching skills as well. The more you are able to learn as a youth basketball coach, the more you are going to be able to pass on to your players. So make sure to take advantage of all of the basketball learning you can. Whether it is reading books, online basketball resources, or DVD's, always continue to be learning and growing.
The more you are able to learn as a youth basketball coach, the more you are going to be able to pass on to your players. So make sure to take advantage of all of the basketball learning you can. Whether it is reading books, online basketball resources, or DVD's, always continue to be learning and growing.
So, hopefully, this checklist of different areas that you can be focusing on with your players will help you do the same. Because regardless of what level you coach at, we all have a responsibility to help develop our players as best we can.
8 Tryout Tips Guaranteed to Get You Noticed (And What To Avoid So You Don't Get Cut)
Do you know exactly what the coach is looking for in tryouts? Do you know everything you need to do?
You may think that you do, but its highly unlikely.
Actually, what you think would help with tryouts may be the exact reason you get cut from the team. Sad thing is that Ive seen players like you make these critical mistakes over and over and over again.
Ive been fortunate to conduct tryouts for youth clubs with over 400 kids. Ive also been part of high school varsity tryouts with 100 kids for a state championship caliber team at the high school level.
Im able to give you the critical tips that can help you make the team and avoid those mistakes that get you cut.
Like this article? Download it as a free PDF! (Download Now!)
1. Do what you do well.
One of the biggest mistakes you can make is trying to impress the coach by doing things that are outside your skill set. This often results in a disaster for you.
If you are a good rebounder, grab every rebound.
If you are a good shooter, shoot when you are open.
If you are a good finisher, attack the basket when a lane is open.
If you are a good ball handler, make the simple passes, the simple moves.
If you are not a good 3-point shooter, dont step out and shoot one during tryouts. Ive seen kids literally hit the side of the backboard trying to do this.
Ive seen kids literally hit the side of the backboard trying to do this.
The coach will instantly think, Wow. This kid does not know a thing about shot selection. Maybe hes a low IQ kid.
Trust me... with the limited time that a coach can see you... this is not the impression you want to make. Even if you play great the rest of the time, the coach already has impression about you and thats hard to change.
Here is a good measure... can you make 7 out of 10 shots unguarded from a spot. Maybe 6 out of 10 for youth players. If not, dont take the shot at tryouts.
2. Hustle! Hustle! Hustle!
There is no excuse for any player on this one. You just have to commit and develop that mentality.
When the ball is on the floor, dive on the floor. Box out on every shot. Sprint on the fast break. Sprint to spots on the floor on defense.
Communicate on defense and offense. Be loud and do it often.
Be loud and do it often.
These are things that every player can do and every player should do.
This is why you see players who arent skilled make the team. Theyre willing to do the little things that make teams good or great.
3. Dont be just one of the guys in the crowd - Make a great first impression.
Here is a great way to make a first impression.
When the coach calls everybody in at the beginning of the first tryout...
Instead of walking out there or jogging out there like every other kid.
Sprint! Sprint directly to the coach and stand right in front of him. Stand tall and keep eye contact on the coach during the entire talk.
I guarantee youll have the coachs attention. Ive conducted tryouts. Ive been in rooms with coaches discussing who to cut. This makes a difference.
Your buddies may give you some crap, but youll be the one laughing when you make the team or get more playing time than them.
4. Avoid the amazing play mentality. Do something that makes you stand out in a positive way.
This is not what you think. This is not making an amazing play. Remember... do what you do well.
Flashy doesnt impress coaches. It may look cool on the playground, but thats why you dont see NBA guys doing streetball moves during games. Its flash. Its hype. Its not effective against good players.
You should do something with substance that coaches will notice in a positive way.
Earlier, I mentioned communicate on defense.
One time when I was conducting a tryout for 3rd to 8th graders, we were with the 4th grader session.
All of the sudden, across the gym, I hear a blaring yell Screen! Screen! Screen! It was from this little guy named Tommy.
Ten seconds later, I hear Tommy yell again, I got ball!
This continued the whole day. He communicated early. He communicated loud. He communicated often. (ELO Early Loud Often. Kevin Eastman would have been proud.)
He communicated early. He communicated loud. He communicated often. (ELO Early Loud Often. Kevin Eastman would have been proud.)
There may have been 30 other kids communicating in the gym, but he is the only one I remembered. I didnt know him before the tryouts, but I sure know him now. Guess what... he made the first team.
5. Dont be shy Talk to the coaches before tryouts.
Too many make the big mistake of being too shy to talk to the coach. And this can make a huge difference with making the team.
Sometimes, this simple act will elevate you in the eyes of the coaches because they know that you care and youll do whatever it takes to help the team.
Be specific. Tell the coach that you really want to make the team. Ask them what they need on their team.
6. Be a great teammate Great attitude and sportsmanship
Every coach wants a player who is a great teammate and makes the players better around them.
You can do this by...
Being a great practice player and challenging your teammates during practice to make the team better.
By putting everybody in a better mood with your positive attitude. Lets face it... were all humans and its more enjoyable to have a little fun in life. Nobody wants to be around a person with a poor attitude.
Display great sportsmanship. When a coach sees you helping players off the floor and playing hard but clean basketball, they know that they can count on you not to lose your cool and hurt your team in a negative way at an important time.
7. Get there early / warm up properly.
Getting there early shows the coach that you care and that he can depend on you to show up on time to practices and games.
Also, make sure to warm up prior to playing, so you are playing your best as soon as the whistle blows. First impressions are very important.
8. Who cares if you screw up Next play!
If you make a mistake... oh well, it happens. Everybody makes mistakes.
Always go on to the next play.
The best players react in a positive way to those mistakes and dont let them snowball into a bunch of mistakes.
There are no guarantees in life. However, if you use the tips mentioned above, you will dramatically increase your chances to make the team and earning more playing time.
If you are serious about becoming a better player, we offer Basketball Camps throughout the country during the spring, summer, and fall.
To check out the different camps, Click Here.
Recommended DVDs & eBook:
|
|
The Attack & Counter Skill Development System
This eBook & DVDs will improve your shooting, ballhandling, footwork, perimeter moves, post moves, finishing, aggressiveness, quickness, confidence, mentality, and your all-around game!
Designed by NBA skills coach Don Kelbick, this unique and comprehensive system is incredibly simple when compared to other skill development programs. Yet it works with NBA and pro players at the highest level... (more info) Yet it works with NBA and pro players at the highest level... (more info)
|
What do you think? Let us know by leaving your comments, suggestions, and questions...
Basketball training in elementary grades.
Prepared by the teacher of physical culture Rylkov G.V.
Since the 2002-2003 academic year, along with the current comprehensive program, several alternative physical education programs have been introduced for students of general education schools. And so, working on a complex program, I decided to use one of these alternative programs,
which is based on one of the most massive and popular sports among schoolchildren - basketball, but can only be used in elementary school starting from the 2nd grade, since the comprehensive curriculum for teaching this sport does not provide for elementary school, although passing the section "Outdoor games" schoolchildren master some skills in possession of the ball. A certain role in my decision was also played by the fact that our elementary school works according to experiment 1-4, and therefore I, as I work and in grades 2-3, have to look for and solve something different, new.
A certain role in my decision was also played by the fact that our elementary school works according to experiment 1-4, and therefore I, as I work and in grades 2-3, have to look for and solve something different, new.
Their program material of the alternative program, I used in my work two educational sections "basic knowledge" and "Special training", and included them in the section "Outdoor games" for grades 2-3. And now in my work in this direction began to include three stages in teaching this sport:
Stage 1 - 2-3 classes
Stage 2 - 5-8 grades
Stage 3 - 9-11 grades
Why this sport and not another I chose in my work. Firstly, basketball has become a traditional sport at school for a number of years. Secondly, I myself used to be engaged in game types and basketball is more familiar to me.
And thirdly, the technical and tactical actions inherent in basketball are fraught with great opportunities for the formation of vital motor skills and the development of children's physical abilities.
But I will dwell in more detail on teaching basketball in elementary grades.
Starting from the 2nd grade, students master throws, catching, passing small rubber balls to a partner, stopping in motion on a sound signal and various exercises that develop motor skills. We study all these elements in different ways, but the most acceptable one is through games, for example, “Ball to a Neighbor”, “Passing the Ball in Columns”, “Ball to a Neighbor”, etc. Also in the lessons I use small sports equipment, mostly for personal use, these are small rubber balls , cubes, weighted bags.
Performed exercises with these objects in walking and running, on the spot, in the lid, throws and catching in pairs, students develop the skills that they need later when handling a basketball.
Starting to study some techniques, I introduce the guys to the markings of the basketball court and give them various tasks “Walking along the indicated lines”. To do this, I prepare for them the pace of movement "Hourglass", "Reel", "Snake", etc.
In the class II program, I included the player’s stance, the player’s movement in the stance, stop on a sound signal and various sets of exercises with small and large balls. For the harmonious development of the body and coordination of movements, we perform exercises with both the right and left hands, perform jumps on both the right and left legs, and then we complicate the exercises.
I start training from the player’s stance, explain why a stance is needed in the game and show what position should be in the stance: legs half-bent, arms in front of the chest, and I give exercises for training.
1. Line up. Crouching to jump out and land on half-bent legs, legs shoulder-width apart, one set forward.
2. Sit down in a line, jump out and land in a standing position. Immediately after landing on bent legs, run to the opposite sideline. Use the rack in outdoor games "Sparrows and Crows", "Day and Night", etc.
Movement. There are many varieties of movements, but first we learn running facing forward in a straight line, then we master running with a change in direction and speed. After that, we learn running sideways, backwards and their varieties. The basic element is the position on half-bent legs and balance, which is ensured by the half-bent legs of the arms in front of the chest.
After that, we learn running sideways, backwards and their varieties. The basic element is the position on half-bent legs and balance, which is ensured by the half-bent legs of the arms in front of the chest.
Training exercises:
1. Running around the hall on half-bent legs with a sliding touch of one, then with both hands of the floor along the whistle.
2. Oncoming relay races with touching lines and objects on the floor.
3. Running circles with hand touching the line of the circle. Relay races with running circles.
When conducting games and exercises of a technical nature, I use lighter balls, and heavier balls in general educational exercises.
While walking at an average pace, and then when running, we execute the “Stop” command after which the students stop in a wide step position. With the help of various general developmental exercises with small and large balls, we study movements with balls. The same exercises are for the children a means of developing motor qualities.
To master the techniques of the game I use lead-up exercises:
1. Large ball in both hands at chest level. Throwing the ball up and catching it, you can clap your hands behind your back.
2. The same as exercise 1 but with catching after the ball bounces off the floor at different heights6 at the level of the knee, waist, head.
3. Ball on the floor in front of the student. Bend over and put your hands on the ball. Repeat several times.
4. Same as exercise 3, but put your hands on the ball, grab it with your fingers and press it to your chest, straighten up, bend over again, put the ball on the floor, straighten up.
5. Exercises in pairs with the ball.
6. Throw the ball over your head, straighten your arms and catch the ball, pulling your arms to your chest.
In the third grade, students learn to stand, stop by jumping, catch and pass the ball with both hands from the chest from a place, with a reflection from the floor and backboard.
The main task of teaching basketball in grade III is to study the basics of the game technique and consolidate the acquired skills in outdoor games and special exercises. In the course of basketball lessons, I use various types of walking in a squat and half-squat position on the entire foot, on the toes and lateral arches of the foot, jumping with a push of both legs (in a squat and half-squat), changing the direction of movement (straight, back, left, right), alternating them with walking. Then I give a run from various starting positions, sitting, kneeling, alternating slow running with accelerations and stops in the position of a wide ball. After that, we perform various exercises for the muscles of the arms and legs.
Jump stop. By stopping, the student must cancel the forces of inertia and take a position from which he can start in any direction. The basic element is the position on bent legs with a variable body weight on the back standing leg.
Exercises for learning.
1. Building in 1 line. Alternately in the line, jump in place with a stand with the leg extended forward, squat on the standing leg behind with the hand touching the floor next to it, also on the other leg.
2. In a column, one by one, moving around the hall, make stops on sound signals.
3. The game "Tag" (in pairs, or in groups) performing stops with the arrival. The driver catches up with them and tries to overpower them.
Catching and passing the ball with both hands from the chest while standing still. The main element during catching is the position of the hands, reproducing the shape of the ball. Exercises with passing and catching the ball are performed in the player's stance.
Exercises for learning.
1. In ranks of 4-5 people. In front of each line is a driver. The players take a stand. Hands at face level, brushes reproduce the shape of the ball. The driver alternately puts the ball into the hands of the players, having received the ball, the player lowers his hands to his chest and holds in the position from which the transfer is made.
2. Standing in line. The driver alternately throws the ball to the players, doing this from 2-3 m with one hand from below so that the ball flies at face level. The player extends his arms and catches the ball with a step towards.
Dribbling with the right and left hand in a straight line.
The main element is the position of the forearm and elbow of the hand leading the ball, which, as if trying to take a position below the hand, are ahead of the hand. This makes it possible to follow the ball far down and meet it early with a brush, as well as control the ball.
Exercises for learning.
1. Formation in 2 lines. From a stand on strongly bent on strongly bent legs, imitation of dribbling. Start moving down with the elbow and forearm and end with the hand.
The leg is extended forward, the same-named hand performing the lead.
2. Building in a line. Dribbling the ball in place with a change in the height of the ball bounce. The stance is of the same name, the fingers of the hand performing the lead are directed forward.
3. Leading in place with the right and left hand in the right-handed and left-handed stance. During the lessons, I give students various preparatory exercises with the ball, which develop certain motor qualities, such as speed, agility, and also use various outdoor games "Sniper", etc.
Teaching basketball from primary school has a positive result, after all. At this age, a certain base of skills and abilities is laid, and already in the further study of the game, it is easier for students to master tactical and technical elements and techniques.
From my own experience, I can say that by carrying out this form of work, we have achieved good results in regional basketball competitions, where we win prizes.
Article on the topic "Physical training of basketball players" 10-11 grade
Physical training of basketball players
Participation in basketball competitions requires preliminary development of physical qualities, mastering such important motor skills as running, jumping and throwing. Only then does it become possible to master the technique and tactics of the game and effectively use them in competitions.
Only then does it become possible to master the technique and tactics of the game and effectively use them in competitions.
The diversity of the content of play activity requires a comprehensive development of basic physical qualities and functional improvement of the activity of all body systems, which is achieved in the process of versatile physical training. Along with the development of basic physical qualities, special qualities specific to basketball are also brought up.
The development of physical qualities and the mastery of various motor skills have a direct impact on all aspects of the training of athletes, but most of all on technical and tactical training.
The level of development of qualities affects the choice of playing techniques and their biomechanical characteristics. A sufficiently high level allows you to build the movement according to the optimal scheme, which ensures its effectiveness and vice versa - the lag in the development of the leading quality for this exercise is not able to compensate even its most ideal model.
A sufficiently high level of development of physical qualities determines the choice of one or another tactical scheme of the game. Superiority in physical fitness under certain conditions can compensate for the shortcomings in the athlete's skill. Physically trained athletes have a more stable psyche and the ability to overcome mental stress. They have a high degree of confidence in actions, perseverance. High functionality allows them to more easily cope with fatigue, maintain efficiency and, on this basis, achieve superiority in tactical activities.
There is a close relationship between the development of motor qualities (strength, speed, etc.) and the formation of motor skills. The development of motor skills occurs in the process of improving movements.
Physical training is a process aimed at strengthening and maintaining health, shaping the physique of an athlete, developing and improving his physical qualities. The specificity of the content of physical training of young athletes lies in the development of the basic physical qualities necessary to achieve good results in sports.
The specificity of the content of physical training of young athletes lies in the development of the basic physical qualities necessary to achieve good results in sports.
Physical /movement/ qualities are commonly referred to as certain qualitative aspects of a person's motor abilities. The level of their development is determined not only by the physiological capabilities of its organs and systems, but also by mental factors, in particular, the degree of development of volitional qualities.
The study of age-related features of the development of physical qualities in children showed that the development of physical qualities occurs at different times. The values of annual increases are different in different age periods and are not the same for boys and girls, and also differ in relative (if compared) to compare increases in different qualities: the indicators of power static endurance do not coincide with the level of dynamic endurance.
Endurance, coordination of movements, healthy mind and agility are essential qualities of a good player. Modern basketball is one of the most intense games, so each player must be in a state of the highest physical readiness.
Physical fitness can be defined as the state of readiness of the body to play basketball. Training is a means of preparation. It includes the implementation of special exercises, diet, psychological preparation.
Physical development is a natural process of changes in the body, its physical qualities and characteristics, proceeding depending on the internal causes and conditions of human life. Determining the level of physical development is of practical importance in the selection of means, methods and dosage of the load in basketball lessons.
Distinguish between general physical training /OFP/ and special /SFP/.
General physical training
GPT is a process aimed at developing basic physical qualities and improving vital motor skills.![]() Its purpose is to create a general motor fitness, which is used as the foundation of special training.
Its purpose is to create a general motor fitness, which is used as the foundation of special training.
In the process of general physical training, the following tasks are solved: education of basic physical qualities, increase in functionality, expansion of motor skills, increase in sports performance, versatile physical development, stimulation of recovery processes, health promotion.
For this purpose, a complex of physical exercises of general influence is used, thereby creating the basis for the specialized development of individual qualities. Diverse exercises cause faster adaptation and accelerate the course of recovery processes.
A variety of exercises is designed to increase the range of motion.
At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the patterns of transfer and interaction of various qualities and skills. They can be positive, negative and neutral. With an increase in strength, speed increases, coordination and accuracy of basketball players' throws improve. Positive transfer is provided by skills close in structure to the main game techniques, which coincide with the game mode of muscular work.
Positive transfer is provided by skills close in structure to the main game techniques, which coincide with the game mode of muscular work.
In training, open switchgear without objects, with objects (stuffed balls, dumbbells, etc.) is widely used, high and long jumps, throwing, running at various distances and with obstacles, cross-country, acrobatic exercises, weight exercises.
General physical training achieves its goals only under the condition of constancy and continuity. It is an obligatory component in training at all periods of training of athletes, it does not lose its significance even when high mastery is achieved, when its role increases as a means of narrow specialization, providing diversity, switching and improvement of those involved.
In addition to the correct selection of exercises, the correct determination of the amount of physical activity and its distribution during training sessions is also important.
Motor qualities are formed unevenly and not simultaneously. Growth in different age periods is not the same. The highest achievements in strength, speed, endurance are achieved at different ages. The development of motor qualities depends on the functional state of a number of body systems. So, endurance is largely determined by the activity of the cardiovascular, respiratory systems, and the economical use of energy. Under these conditions, the game activity is characterized by a reaction with a choice and a reaction of a moving object, repeated starting accelerations with a change of direction behind the ball, behind the opponent and away from him, replacing some tricks and actions with others, and, finally, performing techniques and tactical combinations at the maximum fast movement.
The methodology for developing the speed of movement is based on a set of special sprint exercises. However, a simple increase in the means of sprinting in experimental exercises during a one-year training cycle after a certain time leads to a drop in the interest of those involved in them and, as a result, to work at speeds below the maximum. Therefore, specific stimulants for the manifestation of speed in basketball players are needed.
Therefore, specific stimulants for the manifestation of speed in basketball players are needed.
The speed of movements, in addition to many factors, also depends on the degree of skill of the athlete. Accurate execution of techniques at maximum speed, as well as at maximum movement speed, is a very difficult skill, because. in these cases, sensory corrections during the execution of movements are difficult.
An attempt to combine high movement speed and not perfectly mastered techniques leads to the fact that either accuracy worsens or speed drops. For basketball, neither is acceptable. Therefore, the use of combined exercises in speed and technique at different stages of training /when techniques are performed directly during acceleration/ in order to develop basketball players is inappropriate. The use of such exercises will be justified only on condition of perfect mastery of techniques based on the initial separate improvement of the quality of speed and technique of the game.
At the same time, it is very important that the preliminary mastery of techniques comes, as experts recommend, at the so-called "controlled" speed //close to the maximum, but not equal to it/.
This allows you to keep the speed-strength structure of the movement, characteristic of maximum speed, and at the same time control the technique of its execution.
However, in the future, combined exercises are necessary, which is due to the peculiarities of performing techniques in the game. Most techniques are carried out in the shortest possible time periods and, as already mentioned, against the background of movement, which ideally should be as fast as possible. Therefore, in addition to achieving high speed and accuracy of performing a single technique, regardless of each other, it is necessary to be able to combine them.
Combinations with a quick change of one by another are most characteristic of play activity. This combination of high speed of movement with the speed and accuracy of performing several alternating techniques is important. This is complicated by the fact that methods of different nature and structure are changing, which cannot be foreseen in advance. These skills are improved with the help of specific means. One of these means is the recommended exercises in speed of reaction and speed of movement with the simultaneous implementation of several techniques that replace each other, as well as special games.
This combination of high speed of movement with the speed and accuracy of performing several alternating techniques is important. This is complicated by the fact that methods of different nature and structure are changing, which cannot be foreseen in advance. These skills are improved with the help of specific means. One of these means is the recommended exercises in speed of reaction and speed of movement with the simultaneous implementation of several techniques that replace each other, as well as special games.
In the process of finding special means for developing speed, a favorable effect of these exercises on the development of dexterity was discovered.
Agility. It is of great importance in all sports, but it is of particular importance in those that are distinguished by complex technique and continuously changing conditions. The definition of dexterity as a physical quality presents significant difficulties for specialists. This is due to the fact that the question is not entirely clear - how dexterity can be measured. The main measurement of dexterity is considered to be the coordination complexity of the action, the accuracy of execution and the execution time.
This is due to the fact that the question is not entirely clear - how dexterity can be measured. The main measurement of dexterity is considered to be the coordination complexity of the action, the accuracy of execution and the execution time.
"Nimble movements" are movements that are very subtle in their spatial accuracy, and in their spatial coordination, along with this, precisely fit into certain, sometimes very compressed, time frames. At the same time, spatial and temporal accuracy and a combination of movements are manifested not only in strictly standard, but also in changeable conditions. Agility is defined as the ability to master new movements, on the one hand, and as the ability to quickly reorganize motor activity in accordance with the conditions of a changing environment, on the other.
There are 3 degrees of dexterity. The first degree is characterized by spatial accuracy and coordination of movements. The second is spatial accuracy and coordination in a short time. The third, highest degree of dexterity is the manifestation of speed and dexterity in the specific conditions of basketball, and in connection with this, the need for parallel work on the development of these qualities.
The third, highest degree of dexterity is the manifestation of speed and dexterity in the specific conditions of basketball, and in connection with this, the need for parallel work on the development of these qualities.
Basketball players need all 3 degrees of dexterity for successful playing activity. Moreover, the most important role is played by the highest degree. Otherwise, no matter how skillfully and precisely techniques are performed under standard unchanging conditions, they will be ineffective in case of sudden continuous changes in game situations.
The main direction in the development of dexterity is the mastery of new various skills. At the same time, it is very important to increase the coordination difficulties that the trainees must cope with, based on the accuracy of movements, mutual coordination and the suddenness of changes in the game situation on the site.
To develop dexterity as the ability to master new movements, any exercises that include elements of novelty are used. And for the development of dexterity as the ability to rationally rebuild motor activity in a short time, exercises are used that require an instant response to suddenly changing situations.
And for the development of dexterity as the ability to rationally rebuild motor activity in a short time, exercises are used that require an instant response to suddenly changing situations.
It is recommended to use exercises similar to competitive exercises with various changes and additions made both to the technique of performing techniques and the content of exercises, and to the conditions and environment for their implementation. The exercises take into account the most common in game activity alternation of movement methods and the nature of accelerations, different start conditions are also used for partners in the exercise / one jumps, the second is in a position of readiness for the start; one in front, one in the back, etc./.
The difference between the starting conditions and the conditions that are solved during movement is an integral feature of the actions of basketball players.
Flexibility - this is understood as the properties of the musculoskeletal system, which determine the degree of mobility of its links. There are active / manifested due to their own muscle efforts / and passive / manifested when external forces are applied to the moving part of the body - gravity, partner efforts, etc. /. Passive flexibility is always greater than active, and in most cases its increase creates the prerequisites for an increase in the amplitude of active movements.
There are active / manifested due to their own muscle efforts / and passive / manifested when external forces are applied to the moving part of the body - gravity, partner efforts, etc. /. Passive flexibility is always greater than active, and in most cases its increase creates the prerequisites for an increase in the amplitude of active movements.
Flexibility depends on the properties of the athlete's articular and neuromuscular apparatus. The most important of them are: the elasticity of muscles, tendons, ligaments and articular bags, the strength of the muscles with which the movement of a body part is performed in a given direction, the shape and degree of correspondence and size of the articular ends of the bones, etc. By improving muscles and ligaments, flexibility increases.
Flexibility depends on age: it is usually greatest in children. Flexibility decreases with age. It is generally accepted that the most optimal conditions for its development are created at the age of 10-16. Flexibility varies by gender. Mobility in the joints in girls and girls is greater than in boys and boys. Boys lag behind girls in the development of flexibility by about 20-30% in a number of indicators. Flexibility depends on the ability of muscles to relax, it changes significantly under the influence of fatigue, and the indicators of active flexibility decrease, and those of passive flexibility increase. This is due to the fact that when the muscles are tired, their strength and elasticity decrease, and the ability to relax worsens. In such muscles, protective tension occurs earlier. Under the influence of active movements /warm-up, stretching exercises/ elasticity and muscle temperature increase, flexibility improves and, conversely, passive rest, body cooling impair flexibility. Flexibility, more than other physical qualities, is affected by daily periodicity / in the morning, flexibility is significantly reduced /.
Flexibility varies by gender. Mobility in the joints in girls and girls is greater than in boys and boys. Boys lag behind girls in the development of flexibility by about 20-30% in a number of indicators. Flexibility depends on the ability of muscles to relax, it changes significantly under the influence of fatigue, and the indicators of active flexibility decrease, and those of passive flexibility increase. This is due to the fact that when the muscles are tired, their strength and elasticity decrease, and the ability to relax worsens. In such muscles, protective tension occurs earlier. Under the influence of active movements /warm-up, stretching exercises/ elasticity and muscle temperature increase, flexibility improves and, conversely, passive rest, body cooling impair flexibility. Flexibility, more than other physical qualities, is affected by daily periodicity / in the morning, flexibility is significantly reduced /.
Flexibility should only be developed to the extent that the necessary movements can be carried out smoothly.
When developing flexibility, exercises are performed in series of several repetitions in each. For movements in the forearm and hip joints from 15-25 /7-8 years / to 30-45 /13-17 years / repetitions in a series. It is advisable to use passive and static exercises when the muscle mass increases significantly and the ligamentous apparatus almost ceases to deform. Stretching exercises are most effective if performed 1-2 times. If the task is to maintain a certain level of flexibility, you can limit yourself to rare exercises.
Endurance largely depends on the strength of muscle tension, expressed as a percentage of the maximum. The smaller the percentage of effort in relation to the maximum strength of the muscles, the higher the endurance will be.
Rapidity is characterized by the latent time of the motor reaction, the speed of a single movement, the frequency of movements. There is not always a reliable relationship between individual manifestations of speed. High speed of movements can be combined with a slow motor reaction. Speed is determined by the mobility of nervous processes, coordination of muscles by the central nervous system, structural features and contractile properties of muscles.
High speed of movements can be combined with a slow motor reaction. Speed is determined by the mobility of nervous processes, coordination of muscles by the central nervous system, structural features and contractile properties of muscles.
Speed - the ability of a person to perform motor actions in the minimum period of time for given conditions. There are elementary /speed of simple and complex reactions, speed of a single movement/ and complex forms of manifestation of speed /speed of movement of a basketball player/.
Improving individual aspects of the speed of a basketball player using generally accepted means is a paramount task. However, this is only one side, it is known that speed in various activities has its own specifics. In basketball, it is due to the fact that its manifestation occurs in continuously changing situations of direct competition with an opponent in speed and with his resistance with a systematic alternation of different sides of speed and their combinations in the presence of confounding factors - interference.
Special physical training
SPT is understood as the process of purposeful development of physical qualities and functional capabilities of athletes, carried out in accordance with the specifics of the chosen sport and ensuring the achievement of high sports results. Despite the commonality of the nature of the game activity of the body, the development of physical qualities. Therefore, along with the general, a narrowly focused development of the athletes' motor abilities is also necessary.
Special physical fitness contributes to mastering the technique of playing techniques, increasing the effectiveness of tactical actions, achieving sports form, as well as improving mental fitness.
Its main goal is the maximum development of strength, speed and other physical qualities in interconnection and unity.
To solve this problem, specially prepared exercises are used with tension, coordination, tempo and rhythm of movement characteristic of the main exercise. For this, exercises of a technical and tactical nature, sports outdoor games are most suitable. The boundary between GPP and SPP is rather conditional, since the effect of exposure depends more on the method than on the exercise used.
For this, exercises of a technical and tactical nature, sports outdoor games are most suitable. The boundary between GPP and SPP is rather conditional, since the effect of exposure depends more on the method than on the exercise used.
The factors regulating the influence of exercises include the degree of tension, the number of repetitions, the duration of pauses.
SFP is based on the GPP of those involved. It is necessary to proceed to the solution of its tasks only after reaching a certain level of general development. This applies both to the annual cycle of training, and to individual stages of long-term training.
The greatest effect in the development of physical qualities is given by the conjugated method of development with parallel or simultaneous improvement of movement coordination and special techniques and development of motor capabilities.
In modern basketball, a high level of body performance or special endurance in various modes of muscle activity is becoming increasingly important. In addition, basketball requires the manifestation of other qualities, it gives a conjugated method of development when choosing training means: speed endurance, explosive strength, dexterity.
In addition, basketball requires the manifestation of other qualities, it gives a conjugated method of development when choosing training means: speed endurance, explosive strength, dexterity.
The similarity of characteristics allows to determine the main characteristics of the exercises used for special physical training. For the development of certain qualities, exercises are used, selected taking into account the patterns of their manifestation. Endurance in this respect occupies a special place, it is improved in almost every exercise, where the task is performed with some tension and for a relatively long time. A certain type of endurance has its own exercises.
General /aerobic/ endurance is developed in exercises of longer duration /7-180min/ and moderate intensity /pulse 130-180bpm/. With age, endurance in both static and dynamic work increases markedly. Since prolonged work is limited by the onset of fatigue, endurance can be characterized as the body's ability to resist fatigue. General endurance is the ability of an athlete to perform various types of physical exercises of relatively low intensity for a long time, involving many muscle groups. The means of developing general endurance are exercises that allow you to achieve the maximum values of the work of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and maintain a high level of oxygen consumption for a long time. Here cross-country skiing, skiing, swimming, long walks, outdoor work /chopping firewood, snow removal, etc./, running at a uniform pace with low intensity /running duration gradually increases from 5-8 to 25- 30 minutes/. The main methods of developing general endurance are the uniform method, various variants of the variable method, game and circular.
General endurance is the ability of an athlete to perform various types of physical exercises of relatively low intensity for a long time, involving many muscle groups. The means of developing general endurance are exercises that allow you to achieve the maximum values of the work of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and maintain a high level of oxygen consumption for a long time. Here cross-country skiing, skiing, swimming, long walks, outdoor work /chopping firewood, snow removal, etc./, running at a uniform pace with low intensity /running duration gradually increases from 5-8 to 25- 30 minutes/. The main methods of developing general endurance are the uniform method, various variants of the variable method, game and circular.
Special endurance /playing/ mainly provided by mixed character /aerobic-anaerobic/. For its improvement, it requires quite long exercises up to 150 minutes of a variable nature with great and maximum intensity / such a mode of work in cross-country running over rough terrain and running with alternating speeds / fartlek /, in games / mobile and sports /.
Anaerobic endurance is necessary in all actions of a short-term speed-strength nature. The value of this type of endurance increases as the intensity of game actions increases. Anaerobic power determines jumping ability, running speed, throwing power.
Increased anaerobic endurance can be achieved through maximum power exercises - uphill runs, starts and accelerations, exercises with maximum weights. The duration of their implementation is short at maximum intensity.
Speed endurance refers to a person's ability to perform high-intensity exercise for a given amount of time.
Strength endurance is understood as the ability to overcome a given force stress for a certain time. Depending on the mode of muscle work, static and dynamic strength endurance can be distinguished. Static power endurance is characterized by the maximum time for maintaining a certain working posture /defender's stance, stance when performing a shuttle run, etc. /. Dynamic strength endurance is usually defined by the number of repetitions of an exercise / the maximum number of pull-ups, squats on one leg / or the least number of movements in a fixed time.
/. Dynamic strength endurance is usually defined by the number of repetitions of an exercise / the maximum number of pull-ups, squats on one leg / or the least number of movements in a fixed time.
Special speed. In basketball, the success of sports actions is determined by the speed of simple and complex motor reactions, the time of the speed of movement of single movements in actions related to the speed of response to the external situation of the model of the upcoming movement / readiness potential /, which allows you to prepare in advance the use of mechanisms ahead of events and thereby reduce the time of implementation of the motor action. The advanced presetting creates a system of local excitability. Speed in all specific forms of its manifestation is mainly determined by two factors: efficiency of organization and regulation of motor action.
The development of speed requires increasing the efficiency of the central exercise with movements and functional improvement of the corresponding actuators.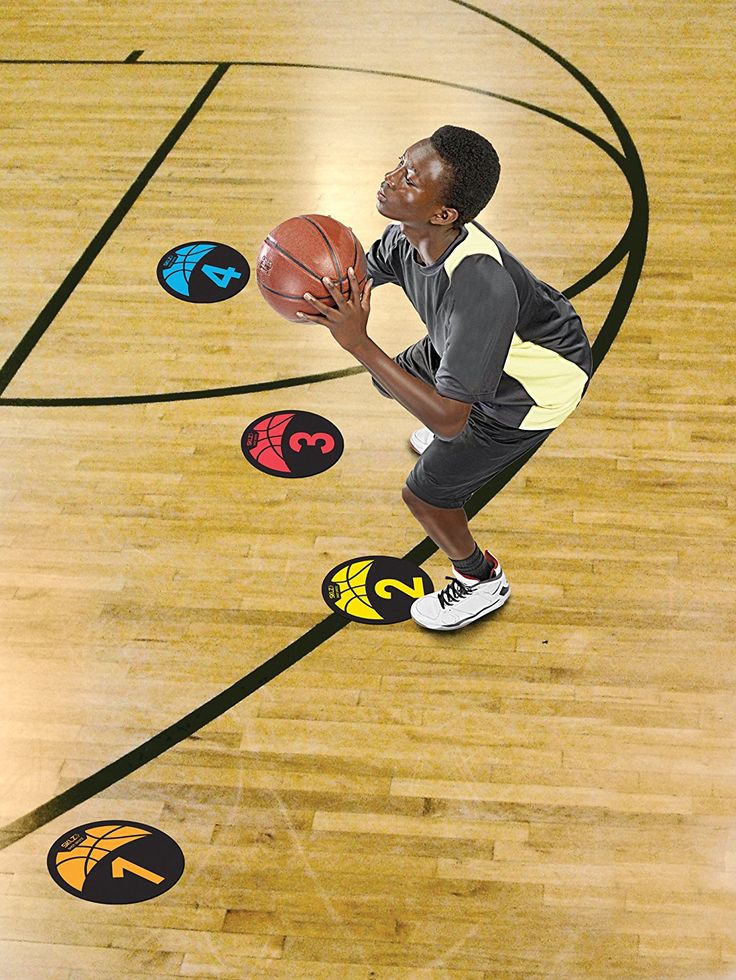
A number of experimental studies testify to the effectiveness of using weights to improve various forms of speed, in particular, the frequency of movement and the latent time of a motor reaction.
Special strength training. Power abilities, which are directly manifested in the magnitude of the working / motor / effort, are provided by a holistic reaction of the body associated with the mobilization of the mental qualities of the functions of the motor, muscular and other physiological systems.
Strength training with heavy weights and low reps mobilizes a significant number of fast muscle fibers, while training with light weights and high reps activates the muscles.
Explosive power . Under the conditions of sports activity, it manifests itself in isometric and dynamic modes of muscle work, and in the latter condition - in overcoming external resistance of various magnitudes. Manifestations of explosive strength are largely related to the previous state of the muscles.
Manifestations of explosive strength are largely related to the previous state of the muscles.
Speed force is manifested in conditions of high-speed movements against relatively small external resistance and is provided by such properties of maximum efforts that determine the starting and accelerating strength of the muscles. To identify the qualitative characteristics of speed strength and in the interests of solving the problem of SPT, it is advisable to consider the fundamental relationship of the speed of sports movements with speed as a general motor ability and muscle power potential depending on external resistance. The connection of the power potential with the speed of the working movement performed against external resistance reveals a slight degree of increase in the magnitude of external resistance.
Means and methods of SFP. The means of SFP include exercises that, firstly, correspond to a competitive exercise in terms of the mode of operation of the body; secondly, they contain training effects in order to increase the level of functionality that the body already has; thirdly, it provides the necessary energy base for improving technical and tactical skills.
It is well known that any tool, depending on the conditions and method of its implementation, can solve a number of problems. Therefore, a clear understanding of the predominant orientation of the training effect on the body of each tool used in training with a different method of execution is an important condition that determines the effectiveness of SPT.
Let's pay attention to one more circumstance. Contrary to the methodological concepts of past years, today athletes widely use the performance of competitive exercises with a high intensity of effort in training. Along with other advantages, such a technique acts as a very effective way of SFP, because it is difficult to come up with something special in this sense. Therefore, the performance of a competitive exercise in training with maximum effort intensity and high speed seems to be an important means of the SPT system, but requires serious scientific and methodological justification.
In practice, when selecting SPT means, one should be guided by the principle of dynamic correspondence, according to which they should be adequate to a competitive exercise according to the following criteria: muscle groups involved in work, amplitude and direction of movement, speed of movement. Based on some criteria, the initial position, the value of external resistance, and more are determined.
The repeated method provides for the performance of exercises with a high level of one or another qualitative characteristic of movement. Therefore, the total number of repetitions of the exercise is regulated by the moment of a noticeable decrease in the efficiency of movement due to developing fatigue. The rest pause between repetitions should be sufficient to restore the body's working capacity to such an optimal state in which high-quality performance of the exercise is possible. In the athlete's training system, the repeated method implements, as a rule, the developing orientation of the training effects on the body and increases the current level of its functional capabilities.
Circle method is a variant of the interval method. It differs from the latter in a more versatile effect on the body due to the use of exercises of various training orientations and a lower intensity of muscle work. It mainly contributes to the increase, improvement of the functionality of various muscle groups and the activity of morphological changes in the body.
Associated method expresses the methodological idea of the unity of the special technical and tactical training of athletes. This idea is realized by the selection of such means and methods of their implementation, which provide the possibility of simultaneously solving the tasks of the SPT of improving the elements of sports equipment. At the same time, SFP funds are selected based on the principle of dynamic matching.
Competitive activity modeling method provides for the intensification of the body's work regime in training due to its maximum approximation at certain stages of the annual cycle to the conditions typical for competitions. The essence of the method is expressed in the holistic performance of a competitive exercise at a high, but mastered by the athlete, intensity level and taking into account the conditions and rules of the competition. Such a technique has an effect on the body that is adequate to the competitive effect, and allows you to effectively solve the problems of SPT, as well as the technical, tactical and psychological improvement of the athlete.
The essence of the method is expressed in the holistic performance of a competitive exercise at a high, but mastered by the athlete, intensity level and taking into account the conditions and rules of the competition. Such a technique has an effect on the body that is adequate to the competitive effect, and allows you to effectively solve the problems of SPT, as well as the technical, tactical and psychological improvement of the athlete.
Control method SFP combines intense training effect in a specific motor mode with an assessment of the degree of preparedness of the athlete's body for this mode. In the control method, a holistic exercise is performed, its simplified version, an exercise that is close to it in terms of the motor structure of functional capabilities. Such an exercise should be standard in terms of the nature of movements and conditions of performance, which makes it possible to observe the dynamics of the performance and functional reactions of the athlete's body over time.