Home »
Misc »
How to break full court press defense in basketball
How to break full court press defense in basketball
A simple, effective and flexible full-court press break
Attacking and breaking full-court pressure defense is no different than attacking any other kind of defense. Emphasize both an attacking mindset and good shot selection. Try to keep everything simple, while providing players with a few basic reads and adjustments so they are able to handle a variety of pressing situations.
Alignment for press breakThe alignment of all five players in this press break provides good spacing and is consistent with their positions in our numbered fast break. This alignment is used against all types of full-court pressure.
DIAGRAM 1: Alignment for press break. 4 always is the inbounder. Teach 4 to move quickly to the inbounding spot outside the backboard with the ball already on the throwing shoulder and with eyes looking down the floor — much the way a quarterback sprints out from the line of scrimmage in football. The point guard (1) initially sets up at the elbow in line with 4 and 5 initially set up at half court where the center circle meets the half-court line.![]() 3 always is on the right side as your team heads down the floor, with 2 always on the left. Both 2 and 3 initially set up close to the foul-line extended. You don’t want them crowding 1.
3 always is on the right side as your team heads down the floor, with 2 always on the left. Both 2 and 3 initially set up close to the foul-line extended. You don’t want them crowding 1.
Entries into playThere are three basic entries out of this press breaker. The first is to 1, which is the primary look against most presses. Talk to 1 about not dancing and moving a lot to get open. Teach 1 to get a good seal and try not to catch the ball below the block, much like you would teach a low-post player when discussing half-court offense. If 1 is fronted, 1 simply walks the defender to the block, seals the defender and 4 lobs the ball over the defender provided there isn’t any backside help. If 1 is being three-quartered or played behind, 1 seals the defender and breaks to the ball.
DIAGRAM 2: ‘Point clear.’ Once 1 catches the ball, the next movements are based on the defense. If it’s a man defense, go with the “point clear. ” 4 curls to the middle of the floor after passing to 1. 5 empties to the opposite free-throw line area. 2 and 3 maintain their 15-18 feet of spacing from 1. Once 1 reads it is a man press, 1 yells “Clear!” and 2, 3 and 4 clear down the court keeping vision with the ball. It is critical for 1 to wait for 4 to curl to the middle before proceeding up the floor with the dribble so that 4’s defender isn’t as readily available to double-team.
” 4 curls to the middle of the floor after passing to 1. 5 empties to the opposite free-throw line area. 2 and 3 maintain their 15-18 feet of spacing from 1. Once 1 reads it is a man press, 1 yells “Clear!” and 2, 3 and 4 clear down the court keeping vision with the ball. It is critical for 1 to wait for 4 to curl to the middle before proceeding up the floor with the dribble so that 4’s defender isn’t as readily available to double-team.
DIAGRAM 3: ‘Point zone.’ If 1 reads the press is a zone, 1 calls “Zone!” and 4 stays in the middle, trying to get the ball from 1, 2 or 3 as those players reverse or skip the ball to one another. 5’s job is to go to the ball-side sideline whenever the ball is in one of the wings’ hands. This gives an additional look up the floor, occupies one of the defenders in the back of the press and opens up the back side of the press. If 4 does catch the ball in the middle, 4 looks at the back-side wing cutting toward the basket (in this case 2).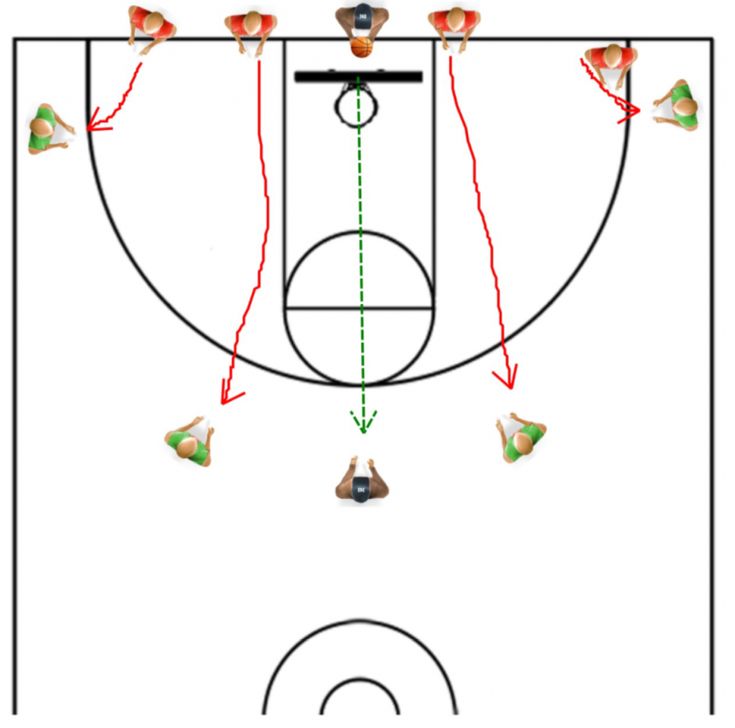 Zone presses tend to have all five defenders on the ball side of the floor, so if 4 does receive the pass from 1, both wings should cut and 4 reads which one is open since the press defenders will not have committed to one side of the floor.
Zone presses tend to have all five defenders on the ball side of the floor, so if 4 does receive the pass from 1, both wings should cut and 4 reads which one is open since the press defenders will not have committed to one side of the floor.
The second entry goes to one of the wings. Have 2 and 3 “V” back to the ball. As with 1, you do not want a wing catching the ball below the block as this is prime trapping position for the defense.
DIAGRAM 4: ‘Wing clear.‘ If 3 catches the ball (as in the diagram), 5 goes to the ball-side sideline in the back court. This avoids the risk of an over-and-back violation. 1 breaks to the middle of the floor and 4 steps in. 3 must read whether the press is man or zone. If 3 reads man press, 3 yells “Clear!” and 1, 2, 4 and 5 clear down the floor keeping vision with the ball.
DIAGRAM 5: Wing zone. If 3 reads zone press, 3 calls “Zone!” and 1 stays in the middle trying to get the ball from 3, 4 or 2 as those players reverse or skip the ball to one another. Once again, 5’s job is to go to the ball-side sideline whenever the ball is in a wing’s hands (once the ball goes from the wing back to 4, 5 slants down the middle of the floor from his ball-side sideline backcourt position to the opposite foul-line area). If 1 does catch the ball in the middle, 1 attacks the press on the dribble, since 1 is the primary ball handler.
Once again, 5’s job is to go to the ball-side sideline whenever the ball is in a wing’s hands (once the ball goes from the wing back to 4, 5 slants down the middle of the floor from his ball-side sideline backcourt position to the opposite foul-line area). If 1 does catch the ball in the middle, 1 attacks the press on the dribble, since 1 is the primary ball handler.
The third entry is called the “5 Entry,” as the ball is being entered to the 5.
DIAGRAM 6: ‘5 Entry.’ If 1, 2 and 3 are having problems getting open, 5 flashes hard to the ball-side elbow. 4 makes a high, two-hand overhead entry pass to 5. 1 and 3 backdoor with 3 continuing all the way to the opposite free-throw line and 1 curling back to the middle of the floor. 5 hits either player, if open. Meanwhile, 4 steps in and 2 holds position at the opposite wing. If 1 or 3 are not open, 5 gets the ball back to 4 and widens out to the wing spot vacated by 3. 3 now takes 5’s press break responsibilities and vice versa.
Adjustments to press breakerDifferent scenarios force you to adjust your press breaker. Try these four adjustments to keep the ball moving into the front court.
DIAGRAM 7: Box. This is used against full-court man defense in total denial. 1 stays at the usual ball-side elbow. 5 is on the other elbow. 3 is halfway between the elbow and the half-court line aligned with 1. 2 is in the same position as 3 on the other side of the ball. When 4 slaps the ball, 1 screens up for 3, who cuts to the right-side wing. 1 then comes back to the ball in the middle of the floor. Simultaneously, 5 screens up for 2, who cuts to the left-side wing. 5 slips the screen looking for the long pass from 4. You now are back in your regular press-break alignment.
DIAGRAM 8: Loop out & fill. This is used against a hard wing trap and denial of the three immediate receivers. 4 passes to 3. 3 now is being trapped. The other three defenders are denying 5, 1 and 4. 1 must release down the floor and loop out to the wing spot. This causes 1’s defender to follow. 2 flashes hard to the area 1 has vacated, gets the ball from 3 and immediately passes to the back side to 1. This should create an opportunity for 1 and 5 to run a 2-on-1 break.
3 now is being trapped. The other three defenders are denying 5, 1 and 4. 1 must release down the floor and loop out to the wing spot. This causes 1’s defender to follow. 2 flashes hard to the area 1 has vacated, gets the ball from 3 and immediately passes to the back side to 1. This should create an opportunity for 1 and 5 to run a 2-on-1 break.
DIAGRAM 9: 21 flash. This is used against a 2-1-2 press. If 4 is being locked up in the press by the middle zone defender, the opposite wing (in this case 3), flashes from behind the defense into the open area to give the defense another look.
DIAGRAM 10: Even. If 1 reads a soft 1-2-2 or 1-3-1 three-quarter or half-court press, morph the press break into a half-court trap offense by calling out “Even!” and having 3 fill the middle, 4 and 5 fill the wings and 1 and 2 fill the guard spots.
Coaching pointsThere are five main coaching points to consider with these press breakers.
1. The end result either should be a layup or a shot in the paint, otherwise, your offense needs to pull the ball out and start the offense. Don’t take quick, long shots.
2. Against man pressure, emphasize to the guards to stay in the middle of the floor as they bring the ball up the court. They also need to make extensive use of the crossover, pullback and hesitation dribble. No spin dribbling! Spin dribbling increases the effect of a surprise trap or a run-and-jump attack.
3. Against zone pressure, emphasize — particularly with the wings — that they must look up the floor after catching the ball. The progression ideally should be middle (to 1), sideline (to 5), skip (to 2 or 3 depending) and back to 4.
4. In practice, work on press breakers more in 5-on-0 rather than 5-on-5. It’s more important for your players to know where they are supposed to be and what their reads are, rather than knowing exactly what an opponent’s press is going to do. Plus, you may not have enough skilled players to duplicate the opponent’s press.
Plus, you may not have enough skilled players to duplicate the opponent’s press.
5. Make sure your players are very conscious of the six trapping areas, or corners, that an effective press tries to exploit.
1-4 Press Break to Score on Any Full-Court Defense
There are many factors that go into winning and losing basketball games:
- Shooting
- Rebounding
- Free Throws
- Press Break Offense
However, at the high school level and below, I don’t think anything will lose a game faster or more frequently than a team’s inability to handle pressure.
We've probably all had teams that have excelled in a controlled half court game, but immediately lost their poise when the opponent began to press.
As a coach, there’s nothing more frustrating than helplessly watching from the sidelines as your team commits countless turnovers when the other team extends its defense.
But it doesn’t have to be this way!
One of the most important jobs a basketball coach has is to equip players with the skills, mindset, and alignments needed to attack pressure.
Each of these elements is crucial – without one, the other two are not nearly as effective.
The 1-4 press break is one sound way of attacking man or zone full court pressure.
Check out the diagrams and options below to see if this type of attack will work for your team.
Utilizing the 1-4 Press Break
One of my favorite ways to attack full-court pressure (man or zone) is with the 1-4 press break.
Below I’ll tell you why you should use it and I’ll show you how it works.
Let’s get started:
Benefits of the 1-4 Press Break:
a. Can be Effective Against Man and Zone PressesThe best press break alignments are versatile. Against a team that changes defenses, you don’t want your players looking to the sideline waiting for a play call. The 1-4 alignment eliminates that confusion because it can be used against any pressing defense.
b. The Alignment Makes Denial More DifficultSome pressing teams try to deny all inbound passes. If your alignment has players deep down the floor, the defense will be able to do this more effectively. By bringing all players up, it eliminates back side help, opening up potential deep passes if the defense denies.
If your alignment has players deep down the floor, the defense will be able to do this more effectively. By bringing all players up, it eliminates back side help, opening up potential deep passes if the defense denies.
c. Forces Opponent’s Post Players to Defend Full CourtThis is another benefit of bringing everyone up against a press. Opponents will need to make a choice: Do I bring up everyone, including a potentially slower post player, or do I just let the ball inbounds? Against many teams, either option could benefit the offense.
d. You Can Attack to ScoreMost 1-4 press breakers eventually send a player down the floor. This still allows your team to hunt layups after it breaks the press. In fact, having a player start high and then break down the floor is more difficult to guard than simply stationing a player deep for the whole possession.
e. It’s FlexibleThere are many things you can do out of a 1-4 alignment. We will show a few options in the next section, but you can use your imagination to adjust the press breaker to fit the personnel on your team.
We will show a few options in the next section, but you can use your imagination to adjust the press breaker to fit the personnel on your team.
1-4 Press Breaker Options:
Option #1: 1-4 Alignment vs. Zone PressureCommon zone presses include the 2-2-1, 1-2-2, and 1-2-1-1 presses.
This alignment can be effective against any of these looks.
Consider the best way to use your personnel.
For example, do you want your point guard to receive the first pass, or would you rather he or she attack up the floor on the second pass?
In the diagrams below, notice how the offense maintains sideline, middle, reverse spacing.
In these diagrams, the fifth player is used in the “deep diagonal” position.
If the ball is reversed, players fill both sidelines and the middle.
Option #2: 1-4 Alignment vs. Man-to-Man PressureAgainst man pressure, you probably want to set screens to help your players get open.
This can be done in many ways, but one option is diagrammed below.
Again, players can be positioned however suits your team, but notice one important detail in the diagram:
Player 5, typically a post player, sets the second screen for Player 1, the point guard.
This is usually a good idea because two advantages could be created against a switching defense.
First, your point guard will usually be quicker than the opposing post player.
Second, your post player should be able to seal an opposing guard.
Another possibility is for Player 5 to screen his or her own defender, making the switch more difficult.
If the ball is inbounded to a good ball-handler, you can clear out of their way vs. a man-to-man defense.
Some defenses will not trap, instead choosing to pressure the ball handler 1-on-1.
If this is the case, your guard should not have trouble and it is better to give them space.
Some teams will let the ball handler start to dribble, then will leave from another player and trap. This is where the pullback dribble is necessary.
This is where the pullback dribble is necessary.
In the diagrams below, notice how, as the trap occurs, Player 1 uses a few pullback dribbles and the other teammates are “pulled” to the ball handler into the sideline, middle, reverse position.
Option #3: 1-4 Alignment vs. Extreme DenialTeams that completely sell-out to deny the inbound pass can be very difficult to play against.
While the second option can certainly be effective against these teams, you may want to have another option as well.
This look is good for teams that negate your screening actions with effective switching.
For example, athletic teams with five players of similar size and quickness may be able to switch without giving up significant size or speed disadvantages.
Against those teams, it may be smarter to maximize space rather than setting a lot of screens.
In the diagrams below, the defense is in a full court man-to-man face-guarding defense with the inbounder’s defender playing “centerfield.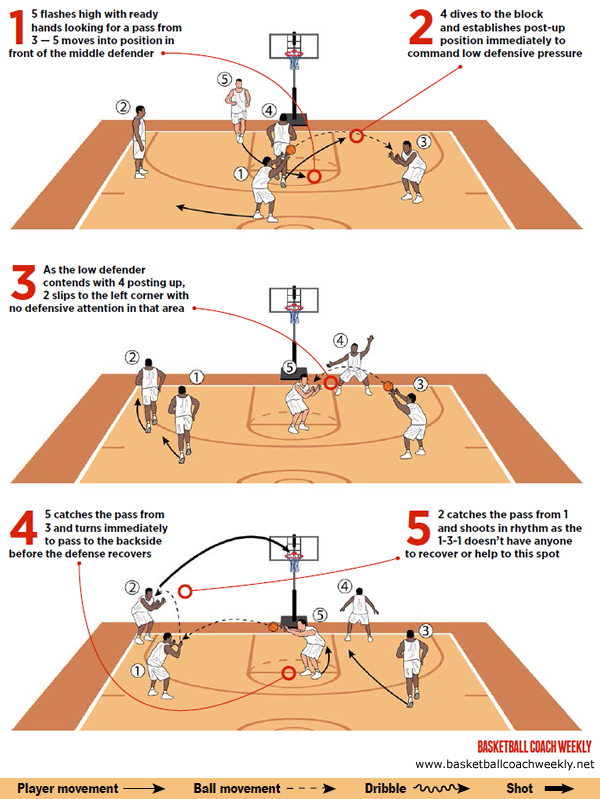 ”
”
The offense counters by all four potential pass receivers walking their defenders as close to the baseline as possible. This shortens all passing options and creates even more space to operate.
Once the ball is inbounded, all offensive players should have an advantage.
The ball-handler can simply read the centerfielder and pass the ball ahead.
This is a great way to alleviate pressure by forcing the defense to become less aggressive.
8 Press Break Tips and Skills to Master:
a. Screen and Seal vs. DenialNo press breaker will be effective if you can’t inbound the ball safely.
If you’re facing a team that denies the inbound pass, you probably want to utilize screens to help free your ball-handlers.
However, your screeners MUST be ready to receive a pass after screening.
This is because many pressing defenses will switch all screens.
If a player screens a teammate’s defender, he or she should pivot in a way that keeps the switching defender on their back.
b. Screen Your Own Man vs. SwitchesAnother strategy against a switching defense is to screen your own defender.
Think about it...
If the defense wants to jump out and switch on all screening actions, screening your own defender makes it difficult for them to do that.
This type of screen can free a teammate to receive the ball.
c. Run the Baseline After MakesFinding a good inbounder is sometimes difficult.
One simple habit to teach your inbounders is to run the baseline after a made basket by your opponent.
If the strong side of the floor is not open, the inbounder can run to the other side to explore options there.
This shortens a potential pass to the opposite side.
d. Sideline, Middle, ReverseThis is a crucial part of attacking man or zone presses that like to trap.
Any time there is a trap, you want (1) sideline, (2) middle, and (3) reverse options.
Some coaches like the fifth player to be diagonal, while others prefer him or her to be deep.
Regardless, these first three options are essential.
This is because it is very difficult for the defense to put two players on the ball while still covering sideline, middle, and reverse options.
With proper spacing, the player being trapped must simply remain poised and find the open teammate.
e. Use Ball FakesFull court presses are, by nature, aggressive defenses.
Jumpy defenders can be moved and manipulated with clever ball fakes.
If you want to pass to the middle, fake a pass up the sideline, or vice versa.
Ball fakes can take some of the aggression out of a defense.
f. Pullback Dribble vs. TrapsThis is the most important type of dribbling against trapping defenses.
Many man or zone presses attempt to bait the ball handler into dribbling before coming to trap.
This is fine.
Good players don’t mind being trapped because they know that traps create openings for the offense. However, you must create space to make those passes.
Pullback dribbles allow you to get that space.
Execute a pullback dribble by turning your shoulders so that the ball is behind you, putting your chin on your top shoulder so that you can see the floor, and taking big push steps back to create space.
As a ball handler uses a pullback dribble, his or her teammates should come back to the ball to shorten the pass. Think of it as the ball handler pulling teammates toward them.
Skilled ball handlers may be able to pullback and attack the other direction off the dribble (“pullback and reattack”), but most players will want to beat the press with the pass.
g. Play With Your Eyes UpThis sounds simple, but it is harder to execute when facing a double-team.
Players must be trained to maintain vision of the floor.
Most full court presses leave a player, sometimes multiple players, open down the floor.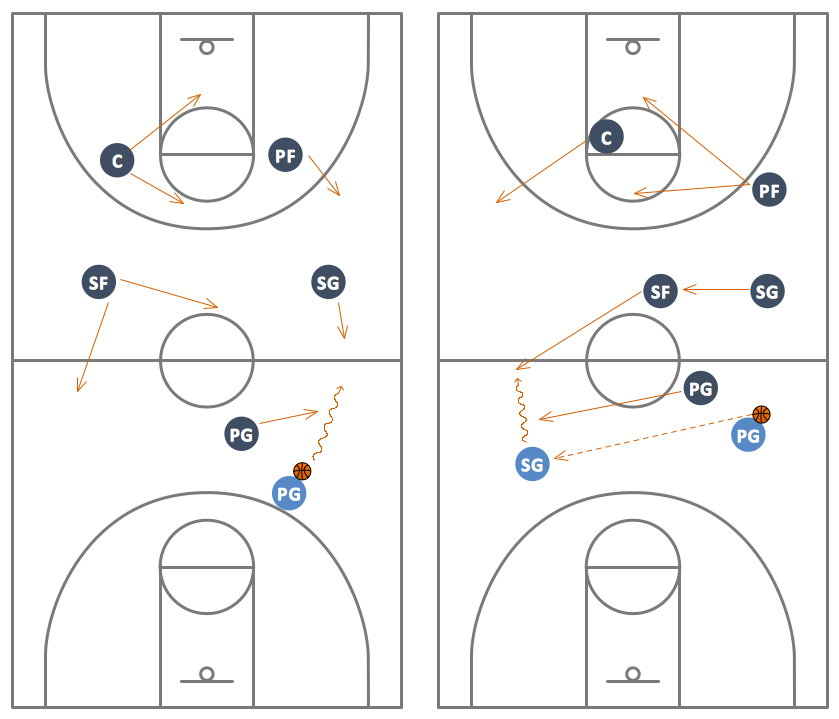
The problem is that ball handlers panic and simply don’t see them.
Emphasize vision in practice and reinforce it through the use of film so that your players learn the importance of seeing what options are available.
h. Score Early or Late in the ClockTeach your players that the goal of press offense is to SCORE!
If you are content with simply getting the ball across half court and running offense each possession, there is no risk for the defense and they will just press more aggressively.
However, shot selection is crucial when playing against full court pressure.
Your first priority should be attacking the press for a layup.
If a layup (or a quality shot from a good shooter) does not materialize, then you can run your offense and seek a better shot.
Remember, many pressing teams want to speed you up.
If your press offense only creates quick long-range jump shots, you are probably playing right into the hands of the defense.
Conclusion:
At some point in your season, you will encounter a team with strong full court pressure.
Will your players be intimidated, or will they feel prepared to attack the defense for layups on the other end?
By emphasizing the proper skills, mindset, and alignments, you can prepare your team to excel in these high-pressure moments.
Press Defense | Basketball team defense
Pressing defense is best initiated after a shot or free throw. There are two types of pressure defense - personal and zone pressure. Each type can be applied to the entire site, three quarters of the site or half of it. Full-court pressing may begin when the ball is put into play from out of bounds, or when the first line of defending players begins active play at the opposing team's free-throw lines. Three-quarters pressing begins at the top of the opposing team's free throw area. Half court pressing starts one step before the line dividing the court into two halves.
The term "pressing defense" implies the use of offensive, attacking defense tactics. Its purpose is to upset the opponent's game, cause inaccurate passes of the ball, violation of the 10 second rule and deprive him of the initiative. The successful use of this defense requires good physical preparation of the players and a thorough study of the technique of defensive techniques.
The use of pressure defense places special demands on the team. The team needs a long bench and sufficient training time to improve both personal and zone pressing. Zone pressing throughout the court is more effective than personal pressing in most cases, since one good dribbler can destroy personal protection. A weak defender in personal pressing, usually an inactive winger, will not be able to counter even a mediocre dribbler.
Team pressing on the court is necessary when the game situation requires immediate possession of the ball. Urgent possession of the ball is mandatory when a team is down by one or two points with a few seconds remaining in the game and the opponent "freezes" the ball. As shooting performance continues to improve (now the highest percentage of hits in the history of basketball), the quality of ball possession is deteriorating. Therefore, defense by pressing can interfere with the effectiveness of the attack, increasing the number of ball turnovers in the opposing team.
As shooting performance continues to improve (now the highest percentage of hits in the history of basketball), the quality of ball possession is deteriorating. Therefore, defense by pressing can interfere with the effectiveness of the attack, increasing the number of ball turnovers in the opposing team.
Press defense training . The coach must show on the diagrams the principles of interaction between players in personal and zone pressing. After the team members have studied the diagrams, the coach should conduct a theoretical session, using a slate board, if possible, to demonstrate tactical interactions. We need to sort out every detail before moving on to the demonstration on the court and insist that the players ask questions. After reviewing the drawings, the coach shows each player his place on the court with certain protective interactions; the team then does these interactions at a slow pace and finally plays at half strength against a weak sparring partner.
Pressing should be practiced daily, and introduced into the game only after the players have reached perfection. First, the coach introduces pressure in game situations where the team is not at risk of losing by applying it, or as a last resort in a losing game when an unexpected change of tactics is required. Usually players master personal pressing faster than zone pressing.
- Personal pressure protection
- Zone pressing defense
- Basic Interactions in Zone Pressing 1-2-1-1 Three Quarters or All Court
- 1-2-1-1 Zone Pressing Defense Change across the court
- Zone pressing 1-2-1-1 half court
- Use of special exercises
- Trainer settings
- General recommendations
- Benefits of pressing protection
- Deficiencies in pressure protection
Exercises . Daily practice in selected team defensive formations is a must. The coach must frequently use half court drills that include 1) personal defense with two against the ball carrier, 2) aggressive 2-3 defense with two against the ball carrier, and 3) zone pressing 1-2-1-1. It is also important to practice pressing all over the court so that the team can use it in critical situations and be able to attack against this type of defense.
It is also important to practice pressing all over the court so that the team can use it in critical situations and be able to attack against this type of defense.
A. Ya. Gomelsky about strategy and tactics in basketball
copies of swiss watches
Strategy is the main theoretical direction of the whole team's work, which determines the means and methods of preparation for the main competitions. Four-year plan for the preparation of the USSR national team for the Olympics in Seoul - the strategy of the team in 1985-1988. The strategy also provides for the management of the team during the competition.
Tactics is a part of the strategy that solves the main tasks of training, taking into account specific capabilities - team resources, characteristics of opponents, competition conditions. All this determines the tactical and combination baggage of the team.
When choosing tactics of the game (attack), one should proceed, firstly, from the real capabilities of the players, taking into account, first of all, their strengths, for the disclosure of which combinations are built and learned. Secondly, attack tactics are determined by the strength and weakness of a real opponent in a tournament, match.
Secondly, attack tactics are determined by the strength and weakness of a real opponent in a tournament, match.
I usually discuss playing combinations with the players for whom this combination is designed. I know the strengths of my players, but the players themselves know them even better and can make significant adjustments to the combinations I have proposed.
A.Ya. Gomelsky about playing defense
I believe that defense is the main concern of the coach: firstly, because the victory of the team largely depends on its strength, secondly, because the attack starts from the defense, like from the stove, in- thirdly, because the players themselves never work on the elements of protection, and finally, because the audience, as a rule, does not see it, even journalists often underestimate it.
The best team cannot win without a solid defense. Team defense is built on the individual characteristics, capabilities and mood of all players. Often in training, and even in competitions, individual players show indifference to defensive actions. It always bothered me and even angered me. Yes, the menial work on defense isn't that spectacular - except for things like block shots, rebounds, interceptions.' And many players are not aggressive on defense, they are resting on defense, trying to prove themselves in attack.
Often in training, and even in competitions, individual players show indifference to defensive actions. It always bothered me and even angered me. Yes, the menial work on defense isn't that spectacular - except for things like block shots, rebounds, interceptions.' And many players are not aggressive on defense, they are resting on defense, trying to prove themselves in attack.
I am sure that without great desire, responsibility, initiative, passion, it is simply impossible to defend today.
If the defender allowed the attacker to receive the ball in the danger zone, he has already lost. And how many cases when the center is allowed to receive the ball in the three-second zone under the shield, without striving to actively fight for an advantageous position.
Often defensive players are in no hurry, they do not concentrate their attention and efforts enough on this part of the game.
I want to emphasize that the psychology of defense is one of the most important concerns of a coach, and often more depends on the focus on defense than on technique and physical condition.![]() Doesn't the ability to intercept the ball and win the rebound depend on the mind and the ability to calculate one's strength? If a player goes to intercept the ball, exposing his rear, and slips past the ball, is this not the result of poor calculation, inability to predict, anticipate the situation, think and act responsibly? All this is the psychology of protection.
Doesn't the ability to intercept the ball and win the rebound depend on the mind and the ability to calculate one's strength? If a player goes to intercept the ball, exposing his rear, and slips past the ball, is this not the result of poor calculation, inability to predict, anticipate the situation, think and act responsibly? All this is the psychology of protection.
I believe that a player who is weak and inept in defense causes more damage to the team than a player who is weak in attack. The definition of "good defense is head and legs", while still valid, is incomplete. Fast, tenacious, active hands that can both hit and intercept the ball, and prevent a throw, pass, kick the ball while dribbling - are no less important for a defender
Counterattack
Counterattack is the most spectacular and quick use of all opportunities to achieve result.
Fast play requires high technique. The desire to play at high speeds is commendable and acceptable only if the speed does not exceed the state of the art.![]() Otherwise, there will be more mistakes, losses of the ball than achievements. Therefore, in an effort to prepare a fast break, it is necessary to train the execution of all technical elements at high speeds, using both active and passive resistance of defenders in situations 1-1, 2-1, 3-2, 4-3, 5--4 and with numerical equality.
Otherwise, there will be more mistakes, losses of the ball than achievements. Therefore, in an effort to prepare a fast break, it is necessary to train the execution of all technical elements at high speeds, using both active and passive resistance of defenders in situations 1-1, 2-1, 3-2, 4-3, 5--4 and with numerical equality.
My idea of a counter-attack is not only to move quickly towards the opponent's backboard, but also to quickly transfer the ball to the opponent's backboard with sharp passes, or, if there is no free recipient to receive the ball, by dribbling the ball, actively moving forward. In the final stage of the fast break, players strive to create a triangle in the front line of attack with the apex on the free throw line. There should be a player with the ball, and two other players - to the left and right of him, 4-5 m ahead.
A counterattack is possible in the following situations:
1) when intercepting the ball;
2) when taking a rebound on his shield;
3) after the opponent has made free throws;
4) after winning a dropped ball;
5) after the opponent manages to score the ball.
The best outcome of a fast break is taking the opponent's ring with a numerical advantage, when implementing situations in numerical equality: 1-1, 2-2, 3-3, 4-4. This is easier than beating a 5-5 defense that has already built up its defensive formations.
There are three phases in a counterattack that are equally important for success:
1) the beginning of a fast break - rebounding the ball, first pass, movement of the players, their start;
2) the middle stage of the development of the attack - the transition by the players of the middle line of the field, their advancement;
3) completion of the attack - passing the ball at speed and throwing in close proximity to the backboard.
The timing of the "rehearsed fast break" depends on the speed of the players, the ball passes and the finishing shot. The USSR national team spent 5-7 s on a layered fast break. I think that the schemes of her tactical formations will provide great opportunities for the creativity of coaches working with any teams.
Playing in the USSR national team such powerful and tall centers as A. Sabonis and V. Tkachenko made it possible to carry out a counterattack through one long pass across the entire court.
Center #5, after recovering the ball from the backboard, passes it to runaway #2.
Such an attack was especially successful when building a zone or mixed defense, when one of the defenders or wingers playing in the front line of defense was given the task of running away at the moment of throwing at our ring, in the expectation that the giants would be able to take possession of the ball , bouncing off the shield, and make a long pass across the entire field. Naturally, such a system of counterattack requires special coordination of actions, and its development takes considerable time in the training process.
Development of a quick counter-attack through the middle of the field.
Players #5, #4, #3 are fighting for the ball and, having mastered it, they try to make the first pass to player #2, who passes the ball to player #1. Player #1 rushes forward dribbling through the middle of the court. Players #2 and #3 overtake the dribbler at high speed, form a triangle with #1, and finish the attack with a close range throw if they manage to create a numerical advantage under the opponent's shield.
Player #1 rushes forward dribbling through the middle of the court. Players #2 and #3 overtake the dribbler at high speed, form a triangle with #1, and finish the attack with a close range throw if they manage to create a numerical advantage under the opponent's shield.
If it was not possible to complete the attack in the first echelon, then the second echelon comes into action - center players #4 and #5. They, each on their own side of the court, rush to the opponent's shield. The one on whose side the ball is on ends the attack.
Development of a fast sideline break.
On a rebound from the left side of the backboard, the post makes a quick pass to player #2, who opens to receive the pass to the sideline, just above the free throw line. At the intersection of the sideline with the center, player #1 receives a pass from player #2, then passes it to player #4, who rushes forward on the left side. Player #4 has three possible continuations of the attack: give the ball to player #5 or #3, who is running towards the opponent's backboard in a straight line, or pass to player #2 in the area of the arc. It is clear that the transfer should be made to the most open player, who is in the most advantageous situation.
It is clear that the transfer should be made to the most open player, who is in the most advantageous situation.
A similar situation occurs when attacking on the opposite side.
Development of a fast break after a free throw into our ring.
If player #4 catches a bounce or quickly clears a potted ball from behind the endline, the first pass is to the left sideline to player #1 opening at or slightly above the free throw line. Player #2 opens near the center circle, receives the ball and dribbles forward. Players #5 and #3 pass the dribbler along the touchlines, player #4 overtakes him from the right, and player #2 stays slightly back in the backing position. Thus, player #2 has four options to choose the direction of the attack.
Same procedure as above, but after rebounding a field goal or after the ball is thrown in from behind the end line.
Developing a fast break after a dropped ball in the center circle or on the free-throw line in our half of the field.
Player #5 discounts player #4 who is ready to receive the ball with his hands up. After catching the ball, #4 passes forward to player #1, who opens up to receive that pass after being screened by player #3. Players #2 and #4 support the attack. Such a combination can be played in both directions. At the heart of her success is high growth, good jumping ability and the ability to accurately throw the ball to the partner of the center player.
Same scheme, but now player #4 screens player #2 who, having received the ball from player #3, rushes forward.
The easiest way to complete a counterattack is for the players to take the shortest path to the opponent's shield. However, with the development of a counterattack, options are possible with cross screens
interaction like a trio
setting up screens for the players of the second echelon in the center of the field.
Many teams in the world, including the USSR national team, after they failed to complete the counterattack with a scoring throw, in the transition to a positional attack, spent precious time placing players, thus allowing the enemy to prepare for defensive actions and occupy all defenders advantageous positions. This is why a quick or non-stop attack after a counterattack ("transition game") is increasingly used in the tactics of the best teams in the world. I will give an example of such an attack in the USSR national team.
This is why a quick or non-stop attack after a counterattack ("transition game") is increasingly used in the tactics of the best teams in the world. I will give an example of such an attack in the USSR national team.
The fast break was not completed by the players of the first attack tier #2 and #3, nor the second tier #4 and #5. They, each on their own side, set up screens for fielders #3 and #2 for a shot from medium or long distance, and then go to the backboard to receive the ball in the three-second zone on the spot or to fight on the backboard, after a throw from one of the players # 2 or #3. Options for a non-stop attack can be very different. This could be a double or triple screen for the team's sniper, or a winger or post entering the 3-second zone after receiving the screen. It all depends on the characteristics and capabilities of the player for whom the combination is being made.
Double screen to Marciulionis (#2) to attack with his left hand from the free throw area.
Players #4 (Volkov) and #3 (Tikhonenko) simultaneously put up two screens for player #2 (Marciulenis). #2 breaks into the free throw line, where he receives the ball from player #1 (Sokka). "Marciulionis has opportunities to continue the attack:
a) receiving the ball in motion and passing under the backboard;
b) receiving the ball with a stop and shooting at
c) passing the ball to player #5 (Sabonis) in case there is a switch of defenders.
Players #4 and #2 after screening go under the backboard to fight for the rebound.
Mixed defense
There are several systems of mixed defense:
1. Four players build a zone defense 2-2
or 1-2-1
capabilities and tactics of the opponent.
2. Three players build a 2-1 zone defense and two guard the enemy's strongest snipers.
3. One player completes the zone formation and four players cover the opponents personally.
4. Two players form a zone defense and three players act as an individual defense.
Two players form a zone defense and three players act as an individual defense.
Mixed defense brought good luck to the USSR national team and the CSKA team more than once. The choice of defense has always been determined by the characteristics of the opponent and our capabilities.
In the final of the Olympic tournament in Seoul against the team of Yugoslavia, we used a mixed defense 1-4.
Sabonis played a zone defense, the rest of the players closely guarded their opponents. This was due to the presence of Vrankovic or Raja in the Yugoslav team, who are not very dangerous away from the shield, and the fact that Petrovich, Paspal, Kukoch posed a big threat. The players who guarded the leaders of the Yugoslav team could, with a greater degree of risk, fight with their opponents to get the ball. They knew that Sabonis would help them if they were beaten.
A similar defense was chosen in the semi-final tournament in Seoul against the US team. Sabonis did a zone defense and let Robinson or Reed or Maning shoot from wide. But the rest of the US players were completely covered, and a player like Maning did not bring a single point to the team. As a result, the USSR national team won 82:76. And Sabonis, who participated in the Olympics after a serious injury, two operations, took first place in the selection of balls from shields and made a great contribution to the victory of the USSR team.
Sabonis did a zone defense and let Robinson or Reed or Maning shoot from wide. But the rest of the US players were completely covered, and a player like Maning did not bring a single point to the team. As a result, the USSR national team won 82:76. And Sabonis, who participated in the Olympics after a serious injury, two operations, took first place in the selection of balls from shields and made a great contribution to the victory of the USSR team.
Sometimes, with two centers Sabonis - Tkachenko, we built a mixed, personally set defense 3-2. Two giants and one mobile defender played well in the zone. In the early 70s, it was Eremin, then Valters, and at the Olympics and the pre-Olympic tournament Sokk performed this function, and Belostenny and Volkov played instead of Sabonis and Tkachenko in Holland.
At the Seoul Olympics, we used such a defense (3 in the zone, 2 in person) against the Brazilian team.
Sabonis, Volkov and Sokk built a triangle on top of which Sabonis and Volkov played. Tikhonenko took care of So-uzu personally, and Marciulionis took care of Schmidt, and although these two players scored 65 points together, the match turned out to be very difficult for us, but we still won 110:105. The mistake in the choice of defense was that Schmidt outplayed the smaller Marciulionis in different positions, and Souza outplayed the slower Tikhonenko. In the last 10 minutes of the match, Volkov was attached to Schmidt, Marciulionis switched to Souza, and we changed Tikhonenko to Goborov in zone defense.
Tikhonenko took care of So-uzu personally, and Marciulionis took care of Schmidt, and although these two players scored 65 points together, the match turned out to be very difficult for us, but we still won 110:105. The mistake in the choice of defense was that Schmidt outplayed the smaller Marciulionis in different positions, and Souza outplayed the slower Tikhonenko. In the last 10 minutes of the match, Volkov was attached to Schmidt, Marciulionis switched to Souza, and we changed Tikhonenko to Goborov in zone defense.
Benefits of mixed defense
allows you to fight with him to get the ball, while expecting the active help of teammates, without fear of a throw.
2. Such a system, if the opponent is not prepared for it, tactically introduces confusion and makes it difficult to carry out screening combinations.
3. Combines the best aspects of individual and zone protection systems.
4. Promotes a quick transition from defense to counterattack.
5. Allows players to use their strengths defensively and not show their weaknesses.
Allows players to use their strengths defensively and not show their weaknesses.
6. Can take the point guard out of the game and deprive the opponent of the usual formation and rhythm, destroy the counterattack if applied pressure throughout the field.
Weakness of the mixed defense
1. A technically competent team that has several leaders easily rearranges the offense and breaks the mixed defense.
2. Simultaneous movements of two or three players diagonally can destroy a mixed defense if the opponent manages to create a numerical advantage on one of the sides of the field.
3. Often vulnerable to medium throws from 3-4m.
4. Requires special lengthy preparation, coordinated actions, high teamwork of the whole team for rebuilding and interchangeability in positions.
5. If one of the five players did not have time to reorganize or did not cope with his duties, then the whole idea of such a defense breaks down.
A.
Ya. Gomel. Pressing defense
Pressing is the most active type of defense, constant pressure on the opponent. It can be personal or zone, it can start from the moment the opponent throws it: all over the court, on 3/4 of it, in their own half, i.e. on 1/2 site.
The goal of defense by pressing is not only psychological pressure on the opponent, but also the desire to break the opponent's established game, break his habitual connections between defense and attack, his combinations, make inaccurate passes of the ball, hasty - throws. It is impossible to apply pressure without mastering enough methods of individual protection. This form of defense requires high physical condition, good reserve and teamwork of all players and team units.
Pressing is used both as a system of play for long periods of time, and as a forced measure: when losing in a score to increase the pace or when waiting for pressure from an opponent.
By pressing, we try to take the ball away from the opponent - we force him to make false, inaccurate passes that are easily intercepted. Often, the opponents of the front line of pressing, having missed the opponents, do not pursue them, but watch the development of further events - this is a gross mistake. It is necessary to chase the player with the ball, trying to knock the ball from him from behind, stepping on his heels. Thus, you force the opponent to rush, worry, make mistakes.
Often, the opponents of the front line of pressing, having missed the opponents, do not pursue them, but watch the development of further events - this is a gross mistake. It is necessary to chase the player with the ball, trying to knock the ball from him from behind, stepping on his heels. Thus, you force the opponent to rush, worry, make mistakes.
If in zone or personal pressing you are left without a player and do not help a friend, you make a miscalculation. If one of the five pressers is not active, the work of the entire team goes down the drain. Pressing is primarily an active defense of the team.
In modern basketball, many coaches tend to believe that personal pressing is less effective, difficult, leads to a large number of personal violations and is inferior in usefulness to zone pressing systems. I also believe that a strong, technical player with good dribbling is able to cope with personal pressure.
In addition, with a stretched defense, it would be incredibly difficult to keep such players as Marciulionis, Volkov, Kurtinaitis, Petrovich, Schmidt, Kukach, Paspal, Rivier, Gallis one on one. I'm not talking about NBA players. But although zone pressing has become more popular, it is impossible to do without the ability to play personal pressing. Therefore, it is necessary to train defense daily 1-1, 2-2, 3-3, 4-4 all over the court, with and without the ball, with and without dribbling, with and without screens, first at a walk, then at high speed.
I'm not talking about NBA players. But although zone pressing has become more popular, it is impossible to do without the ability to play personal pressing. Therefore, it is necessary to train defense daily 1-1, 2-2, 3-3, 4-4 all over the court, with and without the ball, with and without dribbling, with and without screens, first at a walk, then at high speed.
Exercises are useful in which the number of defenders prevails over the number of attackers. These exercises promote the interaction of the defenders, instill the skills of tackling the ball. They are also good for attacking players. When training personal pressing, due attention should be paid to the rapid movements of players in an active stance, in different directions, with a skillful change in the positions of players. Defenders of the first line of defense seek to push their attackers to the sidelines and prevent the attacker from getting around him with the ball and without the ball.
If one of the defenders managed to stop the attacker with the ball at the touchline at the intersection with the penalty or center line, the defensive partner must come to the aid of a friend: together they force him to make a cross pass, which the other three players are ready to intercept.
The initial stage of personal pressing is carried out by two fundamentally different tactical formations:
1. The opponent who introduces the ball into the game holds a high moving edge and with an active movement of the hands prevents him from making an aimed pass.
2. No one guards the opponent who puts the ball into play, but two pressers prevent the most dangerous dribbler from getting the ball.
For example, Volkov secured Sokk and Marciulionis from behind when passing to player 5. make him stop and do not let him make an accurate pass, interfering with his hand movements;
2) if the defending partner allowed himself to be bypassed, immediately come to his aid, of course, without leaving your ward in a safe position under the shield;
3) constantly watch not only your ward, watch the actions of partners, learn to see the whole field.
In the USSR national team and CSKA, zone pressing 1-2-1 - 1 brought us the most success. We started pressing from the opponent's front line after a goal and a free kick. High extreme Volkov interfered with the throw-in. If the ball was injected to the right, Marciulionis and Volkov attacked X2 defender together, trying to prevent him from going forward and make an aimed pass to XI defender, Sokk followed the movement of X3 and X4. Sabonis secured the rear, was responsible for long passes and for the X5 player. Tikhonenko in the center of the field followed X4's pass with a long pass and went to the ball passing side.
We started pressing from the opponent's front line after a goal and a free kick. High extreme Volkov interfered with the throw-in. If the ball was injected to the right, Marciulionis and Volkov attacked X2 defender together, trying to prevent him from going forward and make an aimed pass to XI defender, Sokk followed the movement of X3 and X4. Sabonis secured the rear, was responsible for long passes and for the X5 player. Tikhonenko in the center of the field followed X4's pass with a long pass and went to the ball passing side.
Returning with a weak attack, we built a defense 2-3
Zone defense in basketball
The meaning of this defense is that the players are in charge of a certain area of the field, in accordance with the position of the ball and the formation of the attacking team.
Benefits of zone defense:
1. Gives the opportunity to arrange players according to their physical, technical and mental characteristics.
Tall, jumpy players are located close to the shield, mobile, fast players - in positions higher from the shield.
2. More commanding, easy to master, able to compensate for the individual gaps in the defense of the players.
3. Promotes counter-attacking and frequent interceptions of the ball with the greatest possible degree of risk, because. Partners are always ready to help.
4. The number of fouls in a zone defense is usually less than in a personal defense.
5. This defense is less vulnerable to screen combinations.
6. Can concentrate with strong opponent centers and stretch with snipers.
7. More than personal protection, it saves players' strength and protects leaders from fouls.
8. Most effective against opponents with strong centers.
9. A team that owns a zone defense can easily build mixed forms of defense: 3-2, 4-1, 2-3.
10. Convenient and suitable for small fields.
Disadvantages of zone defense:
1. Inferior to the personal psychological responsibility of the players, their charge for individual victory in defense.
2. Less useful against teams with strong snipers.
3. As a rule, the corners of the court are less protected in zone defense.
4. Zone defense can be used occasionally and should not be the main form of defense. It is not advisable to use zone defense at the beginning of the match, when the opponent's players are not yet tired, energetic enough - their throws are more accurate and productive than at the end of the game.
There are several formations of the zone defense, however, each of the zone defenses should easily transform depending on the attack - stretch when attacking from a distance and group around the ring.
Even type of zone defense formations includes systems: 2-2-1, 2-1-2, 2-3.
Odd formation: 1-2-2, 1-3-1, 3-2.
Each of these constructions has its advantages and disadvantages, which are useful to analyze.
The arrows indicate the direction of movement of the players. The shaded places on the court are the weak positions of the defense.
Zone defense 1-2-2
#1 - the lightest, fastest defender, #2 and #3 - quite mobile, jumpy, good if their height is at least 2 m. #4 and #5 - centers. Their task is to fight with the opponent's centers, picking up balls from the shield.
This system is most useful against teams trying to attack from under the shield through the post. Disadvantages - weak positions indicated in the figure.
Zone defense 2-1-2
It is used against strong opponent's centers who are dangerous on the "second floor" when rebounding the ball. Good for developing a counterattack with fast #1 and #2 players. Vulnerable in corners under 45, in the center for long and medium throws. The task of post #5 is to mark the opponents' post and, together with ?3 and ?4, create a rebounding triangle. #3 and #4 are mobile and high wingers, they can be swapped depending on the place of the sniper's attack.
Zone Defense 1-3-1
Helps to keep #3, #5, #2 between the ball and the basket at all times, used against opponent's strong centers and shots from middle and close positions. Her weakness is throws from the corners of the site and passes to the shield along the front line.
Her weakness is throws from the corners of the site and passes to the shield along the front line.
#1 - the fastest defender, running into the gap in every possible situation, #2 and #3 - mobile, jumping players, #5 - center, #4 - the fastest winger, able to move into the corners of the court.
Zone defense 3-2
#1, #2 and #3 are aggressive, mobile players, the success of the whole system largely depends on their activity. All three are focused on intercepting the ball and counterattacking. This system is most acceptable against teams seeking to attack from a distance, and less suitable against strong centers. The 3 second zone and 45 angle positions are the most vulnerable. #1 is in charge of the foul line. #2 and #3 are in a rebound fight. #5 and #4 are the first and second centers.
Zone protection 2-3
Strongest under the backboard, in the corners of the court along the front line. It is used against a tall, powerful team attacking from close positions and from under the shield. Often used for group selection of the ball in the corners of the site. When interacting #4 and #2 or #3 and #1, the defense is less effective on the foul line and at a 45 angle. #5 - center, #4 - second center, #3 - winger, #1 and #2 - defenders, constantly aimed at interception and counterattack.
Often used for group selection of the ball in the corners of the site. When interacting #4 and #2 or #3 and #1, the defense is less effective on the foul line and at a 45 angle. #5 - center, #4 - second center, #3 - winger, #1 and #2 - defenders, constantly aimed at interception and counterattack.
Zone protection 2-2-1
This defense is used by agile and short teams aiming to intercept the ball and constantly counterattack. This zone counterattack is used against teams seeking to attack from medium distances. Center #5 is responsible for rebounding, wingers #3 and #4 are responsible for positions in corners and under 45 , rebounding the ball and for the foul line.
Defenders #1 and #2 tend to close the passes to the shield and into the three-second zone, while they themselves are constantly aimed at counterattacking.
A.Ya. GomelskyDefense against ball carrier
It is necessary to work out the correct position of the body in a basketball stance: the center of gravity is distributed evenly on both legs, but not on a full foot, but on toes, with a "charged" (ready for any movement) foot, knees slightly bent, legs slightly wider than shoulders . Boxing stance - like the great Michael Jordan.
Boxing stance - like the great Michael Jordan.
If the opponent is in possession of the ball, one arm of the defender must be directed at the ball and constantly attack the opponent, preventing him from aiming or throwing (best if it touches the attacker), and the second arm slightly pulled back. Many defenders, being between the player with the ball and the basket, even in the correct stance, do not actively use their hands, do not make an offensive movement towards the attacker, which allows the opponent to calmly take further actions. At the same time, it must be remembered that you cannot cross your legs, that the distance between the defender and the opponent must be calculated so that the opponent can pass with a dribbling to the ring.
Contact defense against the ball carrier, although difficult and somewhat risky, is modern and has its advantages. If your arm extended to the opponent reaches his chest, then by doing so you prevent the attacker from lifting the ball up for a throw.
Defender's movements should be practiced regularly:
a) in each training session - with and without resistance;
b) with one or two balls;
c) with side steps, touching the body with the hand closest to the attacker.
The defender's actions in different situations can be divided into 12 positions:
1. Defense against a dribbler driving the ball to your ring.
2. Defending against a player who has finished the dribble and is looking to either shoot or pass.
3. Defense against an attacker 5-6 m from the backboard, but not using the dribbling.
4. The actions of the defenders in the numerical minority.
5. Actions of two defenders against three forwards.
6. Actions of three defenders against four forwards.
7. Actions of defenders during screenings.
8. Rear screen protection.
9. Slip protection.
10. Group ball tackle by two defenders.
11. Defense against the first pass to the counterattack.
12. Fighting the attacker in the corners of the court.
Let's try to analyze the defender's actions in each of these positions.
1. Defender's task - in a parallel low stance, without crossing the legs, move backwards, knees slightly bent, one hand all the time makes attacking movements towards the dribbler (feints with the body and head participate in this frightening dribbler movement), with the other hand he tries to stop the dribble (if possible, knock the ball out). The raised hand is ready to prevent the presenter from making the pass. Hands can be changed, they are always in motion.
As already mentioned, one should move on a "charged" foot, the heels do not touch the floor, the back is straight, slightly tilted forward, the head is raised up.
The leader should be pushed to the sideline, in the corner of the court, or his movement should be directed towards the defensive partner, remembering that the leader must not be allowed to go to the "strong" side (if left-handed - to the left, if right-handed - to the right).
The distance from the leader should be maintained depending on the speed of his rushing with the ball, his ability to attack or pass, as well as your ability, taking into account the position on the field of defensive partners. Do not rush to take the ball away from a good dribbler, wait for him to stop or make a mistake.
2. If the attacker has finished dribbling and has stopped to shoot or pass the ball, the defender must definitely get close to him, actively using his arms, preventing him from concentrating on the next action. The hand closest to the opponent must touch the fingers of his chest or stomach and not allow him to lift the ball up to attack the ring or pass. The defender seeks to force the opponent to turn his back to the shield and, without stopping attacking the attacker, prevents him from making an aimed pass. The defender must signal to his defensive partners to be ready to intercept the ball. These are already team actions.
3. If the opponent has received the ball 5-6 m from the backboard and he is in possession of the dribble, the defender must not stop actively attacking the attacker; make short lunges with your front foot, use your hands to prevent him from aiming. The attacker cannot be missed to the shield along the front line, if he moves slightly towards it, none of the partners will help the defender. The hand close to the end line insures the passage with the lead, the other one attacks the attacker.
The attacker cannot be missed to the shield along the front line, if he moves slightly towards it, none of the partners will help the defender. The hand close to the end line insures the passage with the lead, the other one attacks the attacker.
Do not give in to feints. If the attacker went to the end line where the defender took up position, you can meet him with his chest and show the referees that he knocked you down. Don't be afraid and learn to fall gently on your back.
If the attacker, despite the activity of the defender, lifted the ball for a throw, you should try to jump with him and prevent the throw. Do not stop working even when the opponent has already made a throw or pass. Do not turn away from him and block his path to the shield. When you take a step back, meet him with your face, and do not try to run after him. You should always be in these moments between the opponent and your shield.
4. If the defender is alone against two attackers, he tries to prevent the ball from being thrown from under the backboard and retreats with his back to his ring so that he can see both attackers. With false movements, he tries to stop the player with the ball and prevent him from making a pass to the opponent under the ring or in time for him in order to block the throw from afar. Not allowing the ball to be thrown from under the shield, the defender will fulfill his mission.
With false movements, he tries to stop the player with the ball and prevent him from making a pass to the opponent under the ring or in time for him in order to block the throw from afar. Not allowing the ball to be thrown from under the shield, the defender will fulfill his mission.
2x1 training on the spot and on the move develops reaction in defenders, teaches active arm movement, backward movement, composure and ability to intercept the ball.
5. Two defenders against three forwards - a common situation in any match, so the defenders, regardless of their position, being in the minority, must know their maneuver.
The front defender moves towards the dribbler to stop him at the top of the three-point offensive zone. He uses a feint, showing that making contact with this attacker is his main real task. At the same time, he should not get close to the opponent leading the ball. The rear defensive player takes a position on the free throw line, behind the front one and, after the pass from the dribbler, moves towards the player who received the ball - he is responsible for passing this player to the backboard or throwing from close range. The front defender, meanwhile, quickly moves to the third striker under the shield, managing to prevent him from getting the ball. The task of the two defenders is to prevent the ball from being thrown from under the shield. Exercises 3x2, 4x3, 5x4 are a good school for practicing such actions. You can train them by attacking with two balls.
The front defender, meanwhile, quickly moves to the third striker under the shield, managing to prevent him from getting the ball. The task of the two defenders is to prevent the ball from being thrown from under the shield. Exercises 3x2, 4x3, 5x4 are a good school for practicing such actions. You can train them by attacking with two balls.
6. If three defenders are defending against four attackers, their actions are built as follows. If attacker XI has the ball, defender ?1 rushes towards him, defender ?2 is responsible for throwing and moving to attacker XZ's shield, defender ?3 moves to the shield. If attacker X2 receives the ball, defender ?1 tends to it. Defender ?3 is responsible for attacker X4, defender ?2 moves to the basket.
A 4x3 drill on the spot and on the move, with rebounding the ball after a throw, with one and two balls - a good rehearsal for a defense of three against four.
7. Today, not a single even very serious team imagines an attack without a combination of screens.
Coordination of actions of the team's defenders, warning about the impending screen determine the preparation of the team to fight the screens.
The guard guarding the screening player must warn his partner of the imminent threat. If the screen without the ball is made by attackers of the same height, there is no great danger of changing the defenders.
If the defenders want to avoid changing when screening from the side, the defender must turn towards the defender and step back, bypassing him from behind, which will not allow the attacker to pass to the backboard.
If the attacker screens from the blind side, from behind, the defender must open towards the defensive partner, turning sideways to him. This will make it difficult to set up a barrier.
8. If your partner puts a screen on the sniper when attacking from medium or long distances behind the defender and you did not have time to get out from under such a screen, a change is necessary: your partner switches to the sniper with his hand raised and prevents him from making a throw. You are left with a dangerous, taller opponent, and your task is to prevent him from getting the ball or picking up the ball after the throw.
You are left with a dangerous, taller opponent, and your task is to prevent him from getting the ball or picking up the ball after the throw.
It is difficult to do without the help of partners in this situation. In general, I am a supporter of the smallest shift with screens, because. this reduces individual responsibility and gives the attacker a chance to beat the defender.
9. If your player, while in possession of the ball, seeks to pass to a teammate who is close to him, you must step back and allow your defensive partner to slip, and then take an active position towards your attacker.
10. The defensive player should always try to get the dribbler to the touchline, into the corner of the court, stop him and turn his back to the backboard.
The second defender, seeing this situation, attacks the opponent with the ball from the other side. Both of them with active hand movements interfere with making an aimed pass. It is important that the rest of the defense players are ready, focused on intercepting the ball.
11. The USSR national team used the defense against the first pass in a fast break more than once against opponents who counterattack through a fast dribbler, sending him the first pass after picking up the ball from the backboard. So we often defended against the Spanish national team, where the ?1 dribbler was Carbolan or Salosobal.
Our team's tall center, who plays close to the backboard, whether it's Tkachenko, Sabonis or Belostenny, prevents the dribbler from making an accurate first pass. At the same time, our fast defender, for example, Homichujus, presses ?1 opponent and does not allow him to receive the ball. The other three of our players were to immediately return to their zone.
So often the counterattack of the Spanish national team failed, in which the Spaniards were especially dangerous and productive.
I must say that there are some significant differences between the game of our and American defenders. According to my conclusions, they are:
1. Americans on the defensive are always offensive, they are not afraid of a contact attack on the attacker in possession of the ball.
Americans on the defensive are always offensive, they are not afraid of a contact attack on the attacker in possession of the ball.
In a low stance with arms raised, the US defender seeks to hit the ball, prevent a pass from being made, not to mention a shot. If the attacker lifts the ball up, the defender immediately reacts to this: his hand rises up and seeks to interfere with any actions of the attacker. The attacker put the ball down - the defender immediately takes two quick steps back, preparing to prevent the opponent's pass without losing his defensive stance.
2. When active, the American defender never allows the attacker to pass with the ball through the center, into the middle, but constantly pushes him to the sideline. When an attacker is missed on the front line, teammates immediately come to the aid of the defender. Our tactic is, on the contrary, to close the baseline, where, as we believe, it is more difficult to provide team assistance. I think it's best to find a compromise here: train the safety net both in the middle of the three-second zone and when passing on the front.